Agent communication
Most agent communication is done with JMS, but some agent activities use the web tier through HTTP(S), as needed.
For example:
-
The server uses JMS to send agent commands.
-
The agent monitor service uses JMS for all server communications and for sending commands, such as "run step," to the worker process.
-
The worker process uses JMS for system communications, and HTTP REST services when performing plugin steps or retrieving information from the server.
-
Agent activities such as posting logs, transmitting test results, and posting files to CodeStation use the web tier through HTTP or HTTPS
-
Most clients use browsers to communicate with the web server through HTTP or HTTPS. We recommend using HTTPS, as it is more secure.
Stateless server-agent communication provides significant benefits to performance, security, availability, and disaster recovery. Because each agent request is self-contained, a transaction consists of an independent message that can be synchronized to secondary storage as it occurs. Either the server or agent can be taken down and brought back up without repercussion, other than lost time. If communications fail mid-transaction, no messages are lost.
Once reconnected, the server and agent automatically determine which messages got through and what work was successfully completed. After an outage, the system synchronizes the endpoints and recovers affected processes. The results of any work performed by an agent during the outage are communicated to the server.
In the following figure, the arrow represents the direction in which the stateless communication was established, but the flow is in both directions with JMS.
Stateless communication
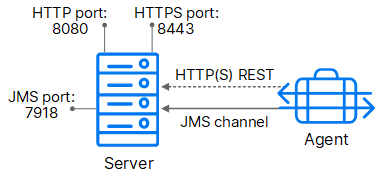
For added security, agents do not listen on ports. Agents send requests when they are ready to make the transition to a new state. Because JMS connections are persistent and not based on a request-response protocol, Deployment Automation does not have to continually open and close ports, which enables the server to communicate with agents at any time while remaining secure and scalable.
REST-style services achieve statelessness by ensuring that requests include all the data needed by the server to make a coherent response.
 See also:
See also: