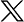Architecture
OpenText Functional Testing Lab is a standalone server that provides mobile device access to different test applications. A distributed architecture where different test clients can all interact with the same server instance is supported.
The environment
The individual components of the OpenText Functional Testing Lab and the relationship between them are represented in the following diagram:
The environment consists of the following components:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Server |
This is a single web server that:
|
|
External PostgreSQL database |
You can connect OpenText Functional Testing Lab to an existing external PostgreSQL database. This allows your organization to manage and utilize existing DB resources. You specify this option during installation. For details, see Windows Installation or Linux Installation. |
| Connector |
The connector is a lightweight piece of software for connecting devices to OpenText Functional Testing Lab, which can be installed together with the server (embedded connector), or as a standalone component. You can install the connector on multiple machines in distributed locations, or on your testing-tool machine. For more details, see Install the connector on a Windows machine, Install the connector on a Linux machine, or Install the connector on a Mac Machine. The connector manages the physical USB connection to the device, and the logical state machine on top of it. It maps the ports to connect to the device over USB and manages the remote screen viewer stream from the device to the tool. It receives lifecycle events from the USB library such as device connected or device disconnected, Agent finished installing, and Agent started. It transfers these events to the OpenText Functional Testing Lab server for adding the device to the pool. The connector is also responsible for installing and uninstalling apps on the device. |
|
Test devices accessed through connectors |
These are the devices (smartphones/tablets) on which the tests are run. The following applications are copied to the test devices:
|
|
NV Test Manager |
Network Virtualization is an optional component for testing apps running under different network conditions. Network virtualization emulates real-world conditions by imposing impairments and constraints in your testing environment during the software testing process, thereby improving software testing accuracy. Supported only for on-premises devices. |
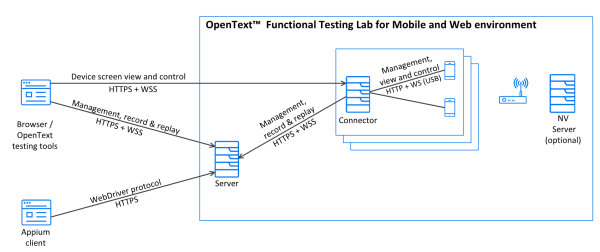
The following diagram displays the OpenText Core Software Delivery Platform (SDP) environment :
Connector deployment scenarios
The connector is a lightweight piece of software for connecting devices to the lab. The embedded connector, which you can choose to install on the OpenText Functional Testing Lab server machine as part of the installation process, is automatically configured to work with the local server. However, the connector can also be installed as a standalone component on a different machine, such as that of a developer or testing engineer. Usually, a combination of the following scenarios is used:
| Scenario | Description | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Central device hub | A central lab of devices connected to the connector on the server machine. | Efficiency. Avoids duplication of tasks for setting up and managing devices. |
| Distributed device hubs | Connectors installed on machines in multiple locations (on-site/off-site/globally dispersed). |
Scalable. New labs can be added as needed. |
| Bring your own device | Connector installed on a developer's/testing engineer's machine. |
Supports hands-on testing of the app on the device. |
Network connectivity
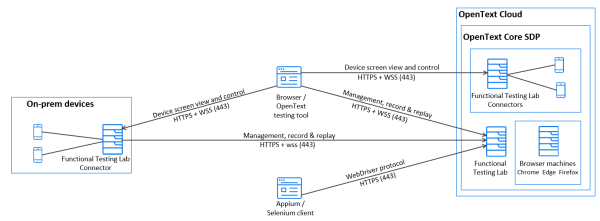
The following diagram represents a more drilled-down view, with a focus on the physical deployment of the server. The different protocols used are also shown.
Client tools and OpenText Functional Testing Lab server connectivity
Common client tools are UFT One, LoadRunner, Sprinter, BPM, OpenText Functional Testing for Developers, and Appium scripts.
Testing-tool clients connect to the OpenText Functional Testing Lab server for the following:
- A user interface (UI) for managing devices and uploading apps over HTTP/HTTPS.
- API (JSON commands) for tests and management, sent over WebSocket (WS).
- The remote screen viewer client.
OpenText Functional Testing Lab server and connector connectivity
The connector establishes a WebSocket (WS) connection with the OpenText Functional Testing Lab server, allowing two-way asynchronous communication from the connector to the server, and vice versa, on the same socket. API calls and files are passed over WS.
Testing tool, connector, and device connectivity
The connector maps a port forward to the mobile device for communication of API traffic using mobile libraries (Android Debug Bridge (ADB), Mobile Device Library (libimobiledevice). It also opens a WebSocket connection to the Agent. The connector maps a port forward for the remote screen viewer. The connector exposes the remote screen viewer directly to the tool for minimum latency when operating the device remotely. The agent on the device listens on a WebSocket port.
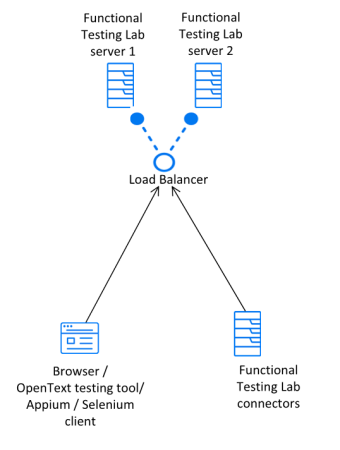
High availability
This functionality is supported only in OpenText Functional Testing Lab.
The diagram below displays an active-passive high availability environment:
Note that both servers should always be up and running. One of the servers marks itself as active, and the other as passive. The load balance redirects all requests to the active server. When the active server fails, the passive server becomes active, and the load balancer starts redirecting all requests to it. Make sure to monitor and restart the failed server, so that it becomes passive.
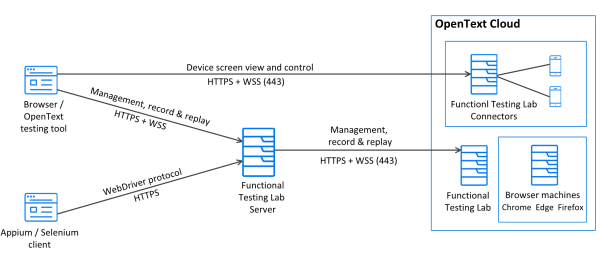
Hosted lab
The diagram below displays an OpenText Functional Testing Lab deployment with OpenText hosted public devices and browsers.
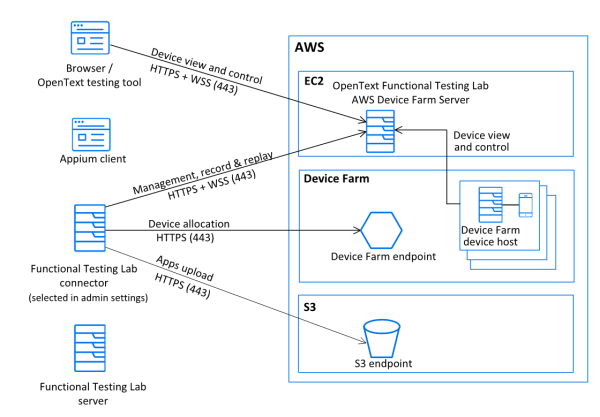
Interface with Amazon Device Farm
You can work with the cloud-based Amazon Device Farm, to run tests on a large variety of devices.
The following diagram depicts how the OpenText Functional Testing Lab connector interfaces with the AWS Device Farm.
For details on how to set up this integration, see AWS Device Farm integration.
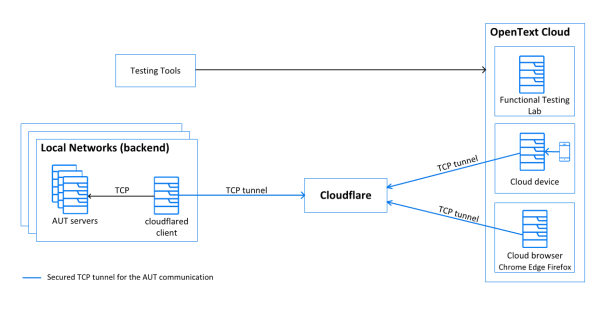
Cloud to local testing
A tunneling solution enables you to use OpenText cloud devices and cloud browsers to test apps hosted on your private networks. The following diagram displays the communication between the elements in the cloud to local testing environment.