Database prerequisites
This section provides an overview of the prerequisites for connecting to an Oracle, Microsoft SQL, and PostgreSQL database server.
Note:
-
Make sure that you create the database user before you start the installation process.
-
Cloud managed databases (RDS) are not supported.
-
Oracle, Microsoft SQL, and PostgreSQL database servers can be set with an IPv4 or IPv6 address. When using IPv6 address, you must use an IPv6 host name and not an FQDN
Oracle Database servers
This section lists the Oracle Database Admin user requirements, client requirements, user profile, and additional Oracle grants.
Oracle Database Admin user requirements
-
To connect to an Oracle database server, the installing database user must have sufficient permissions to perform specific administrative tasks in Oracle. These tasks include creating the project user schema and copying data between projects.
-
If you are unable to use the Oracle system user due to security reasons, we recommend that your database administrator create a database administrative user, for example lre_admin_db, with the specific permissions required to install OpenText Enterprise Performance Engineering.
Your database administrator can create a database administrative user using a script, see this KB article. This script creates the database administrative user with the recommended grants required on the database.
If you are using a container database (CDB), all scripts for creating the database user must be run while directly connected to the CDB. Those scripts must be run by a user with
SYSDBAsystem permissions.Note: When using CDB, the script invokes the "CONTAINER=Current" parameter.
-
The Oracle clients must be installed on the OpenText Enterprise Performance Engineering server with Administrator installation type, and connectivity must be successfully established with the Oracle server.
-
The tnsnames.ora file must contain the net service configuration that has the information to access the Oracle database server.
-
Only a 64-bit Oracle client installation is required.

To install the Oracle clients:
-
Create a root folder for the Oracle clients (
c:\oraclein the example). -
Install the Oracle client 64-bit version within a new dedicated folder (
client_64in the example) under the root folder. -
Copy the relevant tnsnames.ora and sqlnet.ora files into the Oracle clients root folder.
-
Set the TNS_ADMIN environment variable for the Oracle clients root folder (see the example above).
-
Restart the machine.
-
Install OpenText Enterprise Performance Engineering. See Install and configure servers and hosts.
-
Oracle Database considerations: Specify an Oracle user profile
Because every project created in OpenText Enterprise Performance Engineering is a user in Oracle, and each user created needs to be connected to a profile, you must specify a profile for your project to use in the configuration. This profile is added to the user when the Oracle user is created.
-
On the OpenText Enterprise Performance Engineering server, stop the OpenText Performance Engineering Backend Service.
-
Copy the following:
Copy code"SiteParameters": {
"OracleDbUserProfileForNewProject": {
"Value": "",
"Description": "Add the db profile that will be used when creating a new oracle user, value is a string",
"IsSystem": true,
"IsVisible": false
}
} -
Depending on the type of environment you are using:
-
For a clustered environment: To affect all cluster nodes, paste the copied section to the remote appsettings.json file under the repository (for example, pc-repo\SqlEnvironment\system_config\).
-
For a single node: To affect this node only, paste the copied section to appsettings.json in the <repository>\system_config\ folder.
Note: Do not make any changes to the default configuration file, appsettings.defaults.json.
-
-
Add the user profile you want to use to the OracleDBUserProfileForNewProject value.
Make sure that you define the user profile in the same way that it is defined in the database; with or without quotes. When defined with quotes in the database, you must use the escape character ( \ ) in the configuration file.
Example of profile created without quotes:
Copy code"SiteParameters": {
"OracleDbUserProfileForNewProject": {
"Value": "myprofile",
"Description": "",
"IsSystem": true,
"IsVisible": false
}
}Example of profile created with quotes using escape character:
Copy code"SiteParameters": {
"OracleDbUserProfileForNewProject": {
"Value": "\"myprofile\"",
"Description": "",
"IsSystem": true,
"IsVisible": false
}
} -
Make sure that the JSON file is valid and save your changes.
Oracle Database considerations: Add additional Oracle grants
You can customize the configuration file by adding additional Oracle grants to a user if the default grants are not sufficient.
-
On the OpenText Enterprise Performance Engineering server, stop the OpenText Performance Engineering Backend Service.
-
Copy the following:
Copy code"SiteParameters": {
"OracleDbUserExtraGrants": {
"Value": "",
"Description": "Add extra grants to each user created by the app, separate each grant with ';' omit the word 'GRANT' and 'to', will added by the app.",
"IsSystem": true,
"IsVisible": false
}
} -
Depending on the type of environment you are using:
-
For a clustered environment: To affect all cluster nodes, paste the copied section to the remote appsettings.json file under the repository (for example, pc-repo\SqlEnvironment\system_config\).
-
For a single node: To affect this node only, paste the copied section to appsettings.json in the <repository>\system_config\ folder.
Note: Do not make any changes to the default configuration file, appsettings.defaults.json.
-
-
Add any specific grants that you want to give to a user to the OracleDBUserExtraGrants value.
Separate each grant with a semi-colon (;) and omit the words "GRANT" and "to" because they are added automatically.
Example:
Copy code"SiteParameters": {
"OracleDbUserExtraGrants": {
"Value": "EXECUTE ON SYS.DBMS.LOB",
"Description": "",
"IsSystem": true,
"IsVisible": false
}
} -
Make sure the JSON file is valid and save your changes.
Microsoft SQL Database servers
Below is a list of prerequisites that are required when using a Microsoft SQL Database server.
| Prerequisite | Description |
|---|---|
| DB connection permissions |
To connect to a Microsoft SQL database server, the installing database user must have sufficient permissions to perform specific administrative tasks in SQL.
|
| Collation |
Collation for the SQL server must be set to SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS. |
| Connection parameters |
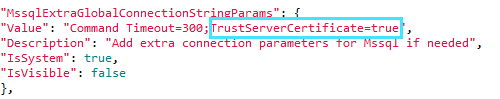
To add additional connection string parameters to a SQL server:
Note: If the certificate installed on the SQL Server is self-signed (which is usually not recommended provided a proper certificate is installed), you need to add
|
PostgreSQL Database servers
To connect to a PostgreSQL database server, the installing database user must either be:
-
A PostgreSQL superuser with "CreateDatabase" and "CreateRole" permissions, or
-
A PostgreSQL non-superuser with the following permissions:
Rolcanlogin = true,Rolcreatedb = true,Rolcreaterole = true, andRolconnlimit = -1.
Notes and limitations
-
Migrating projects from versions 12.6x on Oracle or Microsoft SQL to 202x on PostgreSQL is not supported.
-
If you try to install two environments (such as staging and production or a multi-tenant environment) on the same PostgreSQL database server, they overrun each other.
Resolution: Set up a separate PostgreSQL database server for each environment.
-
The first environment can be configured by running the Configuration wizard. For details, see Configure servers and hosts.
-
For the second environment, you must change the tenant name.
-
Open the appsettings.defaults.json file located in the <Server_installdir>\LRE_BACKEND folder.
-
In the ‘Site’ section, change the “LRETenantName” value to one that is to different to the values on all the other environments.

-
-
-
The first time you install OpenText Enterprise Performance Engineering, and for every time zone change you make on the OpenText Enterprise Performance Engineering server or database, make sure that you align the time zone from the operating system with the time zone in postgresql.conf on the database server machine. Failure to do this results in the Active Reservation/Timeslot ID column being empty in the Hosts grid when you run a test.
To align the time zone:
-
On the database server machine, open pgAdmin. Open lre_<tenant-name>_tenant_db or any OpenText Enterprise Performance Engineering related DB file.
Open a new script and run:
Copy codeSELECT now()Check if there are any differences between the time displayed in the query result and the time of the operating system.
-
Check the time zone set in PostgreSQL by running:
Copy codeSHOW timezoneCheck the time zone on the operating system to verify that a different time zone is set. If the time zones are the same then you have a different issue and there is no need to continue with these steps.
-
Go to <postgresql-install-dir>/<version-of-pg>/data and open the postgresql.conf file. Search for the "timezone" section. You should find the following line:
Copy codetimezone = '<Continent>/<City>' -
Go back to pgAdmin and run the following:
Copy codeSELECT name, abbrev, utc_offset, is_dst FROM pg_timezone_names ORDER BY utc_offset;This should give you a table of all available values that you could put in the postgresql.conf file. Select the name that matches the operating system time zone. Replace the value in postgresql.conf with the chosen value, and save the file.
-
In pgAdmin run:
Copy codeSELECT pg_reload_conf();Followed by:
Copy codeSHOW timezoneFollowed by:
Copy codeSELECT now()It should now display the correct (OS) time zone and time.
-
Run a test and check for Active Reservation/Timeslot ID in the Hosts grid. The problem should be resolved.
-