Synchronizing Project Management and Microsoft Project
How information is synchronized between Project Management and Microsoft Project is based on the type of information and the synchronization mode. There are two types of information involved in the integration:
-
Application-specific information. This is information that is unique to either Project Management or Microsoft Project. Information is recognized by one application but there is no equivalent information in the other application.
For example, Project Management can reference requests and packages, but there is no equivalent type of information in Microsoft Project. Therefore, requests and packages are not synchronized. Likewise, Microsoft Project references resource cost rates but how this information is defined and used is different than cost rates in Project Management. Therefore, Microsoft Project resource cost rates and Project Management cost rates are not synchronized.
Application-specific information is neither updated nor deleted during synchronization.
Note: If a task is deleted during synchronization, all information specifically associated with the task is deleted.
-
Shared information. This is information that can be tracked by both applications such as planned and actuals information.
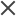
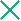
Planned information is the information determined before work begins on a task. This type of information includes task names, task sequence, work breakdown structure, assigned resources, scheduled start and finish dates, scheduling constraints, scheduled duration, and scheduled effort.
Actuals information is the collection of metrics detailing how much time and effort are actually required to complete tasks. This type of information includes actual start and finish dates, actual durations of tasks, actual effort, estimated totals, estimated remaining, percent complete, estimated finish date, and estimated effort remaining.
Table 10-2. How information is synchronized, by information type and synchronization mode and Figure 10-1. How information is synchronized show the type of information and how it is synchronized based on the synchronization mode.