SAP GUI scripting API
OpenText Functional Testing works directly with the SAP GUI Scripting API to record your operations. Therefore, OpenText Functional Testing adds steps to your test or business component only when API events are sent to the server. This means that while recording a test or business component, you may perform several operations on your application before the corresponding steps are added. When you perform a step that sends information to the server, OpenText Functional Testing inserts steps with the relevant Windows-based SAP objects.
In this topic:
Example 1: Checkboxes
Suppose you record the steps of filling in a Price Simulation for Material form. You select the three checkboxes in the form (Incl. cash discount, Delivery costs, and Effective price) and click Continue. When you click the Continue button, information is sent to the SAP server, and the steps in which you select the checkboxes and click the Continue button are added to your test at once:

Example 2: Radio Buttons
Suppose you select a radio button to change the reporting period in the Reconcile Plan Versions transaction of your SAP GUI for Windows application. This radio button is labeled Current Year.
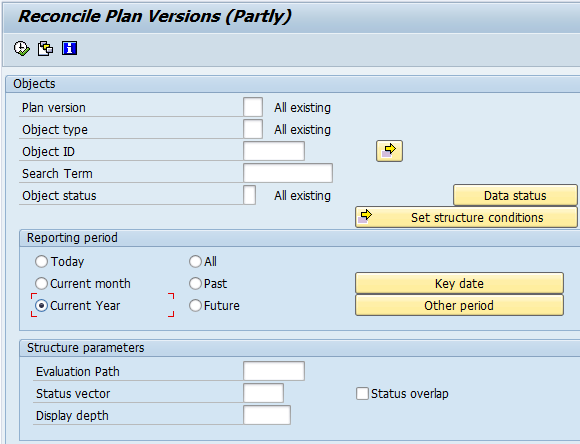
OpenText Functional Testing uses the SAP GUI business component type (41) to identify the object as an SAPGuiRadioButton object. It creates an SAPGuiRadioButton test object with the name Current Year and records the following properties and values as the description for the radio button.
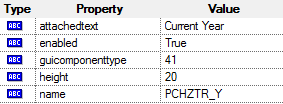
Note: The guicomponenttype and name property values are supplied by the SAP GUI Scripting API.
OpenText Functional Testing also records that you performed a Set method to turn ON the radio button.
OpenText Functional Testing adds a step as follows:
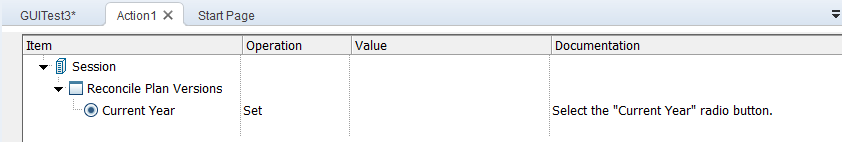
During the run session, OpenText Functional Testing looks up the description for the SAPGuiRadioButton object with the name Current Year by searching the object repository. OpenText Functional Testing finds the following description:
guicomponenttype:=41
name:=PCHZTR_Y
attachedtext:=Current Year
OpenText Functional Testing then looks in the application for an SAPGuiRadioButton object that matches the above description. When it finds the object, it performs the Set method on it to change the value of the field to ON (selects the radio button).