Set up OpenText Functional Testing integration
You can integrate with OpenText Functional Testing through your CI server. This enables you to reflect the tests from your source code management (SCM) repository as executable automated tests. You can then include and run these tests in test suites.
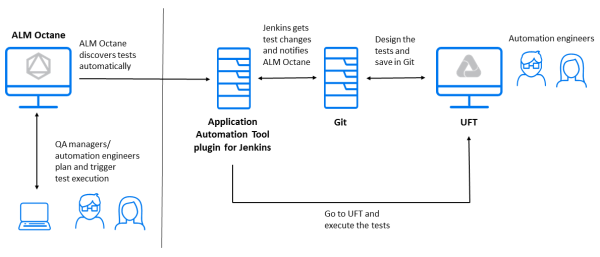
Integration flow
After setting up the integration, the CI server and the SCM system are transparent and you can work with OpenText Functional Testing directly. This enables you to:
- Create and edit your tests and their data tables and save them in a Git or SVN repository.
- Run the tests and track their results.
The integration flow includes the following.
| Action | Description |
|---|---|
| Set up |
To set up the integration, create a CI server and a testing tool connection in the OpenText Core Software Delivery Platform settings. This process is described in the sections below. |
| Test and data table discovery |
Automated test entities are created to represent the GUI and API OpenText Functional Testing tests stored in your repository. The tests are periodically checked for changes in the repository. |
| Associate tests with entities |
Associate the tests with your backlog and application modules. This helps you use the test run results to track your product and release quality. |
| Run tests |
Include the tests in test suites to plan and run them. The test runs are triggered through the CI server. The tests run on OpenText Functional Testing machines configured as Jenkins execution nodes. |
| Analyze release and product quality |
Track the test results as part of the overall data in the backlog, quality, and dashboard modules. |
The image below summarizes the architecture of this integration with Jenkins. For details on supported CI servers, see CI integrations.
Before you set up the integration
Set up OpenText Functional Testing to store tests and data tables in a Git or SVN repository. For details, see the OpenText Functional Testing Help Center.
Follow these integration guidelines:
- OpenText Functional Testing-SCM integration is supported for OpenText Functional Testing 12.50 and later.
-
For OpenText Core SDP to locate the data tables in your repository, store them in an entirely separate folder from your tests.
Set up the connection
In your CI server, set up the connection to OpenText Core SDP.
| CI server | Steps |
|---|---|
| Bamboo |
|
| Jenkins |
You do not need to create pipelines in OpenText Core SDP or create any jobs in Jenkins. However, if you manually create a job to run tests, and tests are located outside of the job workspace, define a parameter UFT_CHECKOUT_FOLDER with the path to the repository root in the file system. This enables OpenText Core SDP to display the test name, rather than the full path to your test. This is supported with plugin version 6.7 and later. |
Add the CI server
This section describes how to add your CI server.
To add the server:
-
Open the Settings menu
 , click Spaces, and select a workspace.
, click Spaces, and select a workspace. -
Select the DevOps > CI Server tab.
-
Add a CI server and select your CI server's URL.
For details, see Add CI/CD servers.
Create a test runner
This section describes how to create a OpenText Functional Testing test runner.
Note: The test runner framework only supports external data tables on OpenText Functional Testing tests of GUI type (and not API type).
To create a test runner:
-
Open the Settings menu
 , click Spaces, and select a workspace.
, click Spaces, and select a workspace. -
Select the DevOps > Test Runners tab.
-
Click + Test Runner.
-
Name the test runner entity to use to run the OpenText Functional Testing tests, and select the UFT framework.
-
Select your CI server.
The list displays all servers that meet the following conditions:
-
The server has the Application Automation Tools plugin installed and configured to access your OpenText Core SDP.
-
The API Access keys that the plugin is using are assigned the CI/CD Integration role in the current workspace.
-
-
Specify the type and URL of the SCM repository that contains your OpenText Functional Testing tests and data tables.
You can create multiple test runners in a workspace, but each test runner must have a separate repository.
-
If required, provide the authentication details for your repository.
-
Click Test Connection to make sure the configuration is correct.
-
Click Save and Connect to complete the connection.
CI server Description Bamboo If you are integrating using Bamboo, two plans are created:
-
UFT One test discovery that connects to the repository and discovers the OpenText Functional Testing tests and data tables.
-
UFT One test executor that runs the tests.
Jenkins If you are integrating using Jenkins, a Jenkins job is created that connects to the repository and discovers the OpenText Functional Testing tests and data tables.
-
Tip: If necessary for troubleshooting, you can find this job on your CI server based on the connection ID.
To enable test runs, see Enable the CI server to trigger test runs.
The test scripts and the data table content are available in OpenText Functional Testing only.
Tests tab
In the automated test entities, the following fields are set.
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| Testing tool type | OpenText Functional Testing |
| Test type | API or UI |
| Executable | Yes. These tests can be added to test suites and run from OpenText Core SDP. |
If you do not see all of the expected tests in the Tests tab, click the Refresh button  to refresh the list of tests.
to refresh the list of tests.
What happens when a test is changed in OpenText Functional Testing
OpenText Core SDP continues to periodically check the repository and updates its entities as follows.
| Change | Impact |
|---|---|
| Add test |
If you add a new test in OpenText Functional Testing or change an existing test, the changes are reflected in OpenText Core SDP. |
| Delete test |
If you delete a test from OpenText Functional Testing, the relevant test in OpenText Core SDP is not deleted but is marked as not runnable. This way, the test and its history, runs, and reports remain available. |
| Rename test in Git |
If you rename an OpenText Functional Testing test in GIT, the test is renamed in OpenText Core SDP if using version 12.60.3 or later, and the test was committed without additional changes. |
| Rename test in SVN |
If you rename an OpenText Functional Testing test in SVN, or if you rename it in GIT and do not fill the above conditions, a new test is created in OpenText Core SDP and the original test is marked as not runnable. |
Run tests on-demand using GitLab
You can use the FTToolsLauncher tool to integrate with GitLab to run OpenText Functional Testing tests in GitLab on- demand. This is supported for GitLab 14.3 and later, including GitLab Cloud.
For details on how to set up this integration, see Running UFT Tests using ALM Octane testing framework (Test Runners).
Link to an automated test
You can create links to drill from your OpenText Functional Testing automated test, directly to the corresponding test in the SCM.
To enable SCM test links:
-
Create an OpenText Functional Testing test runner. For details, see Create a test runner.
-
Define a File in branch template that points to your SCM repository. For details, see Enable links to the Git or SVN viewer.
-
When an OpenText Functional Testing automated test is discovered by the test runner, the test details in it include an SCM test link field. Click the link to go to the OpenText Functional Testing in the repository, based on the template that you set in the File in branch template.
Enable the CI server to trigger test runs
This section describes how to enable the CI server to trigger OpenText Functional Testing test runs for Bamboo and Jenkins.
For Bamboo integration
| Action | Steps |
|---|---|
| Enable Bamboo to run OpenText Functional Testing tests |
|
| Make sure OpenText Functional Testing can run your tests |
|
For Jenkins integration
| Action | Steps |
|---|---|
| Make sure OpenText Functional Testing can run your tests |
|
| Configure OpenText Functional Testing to enable running tests over a disconnected remote connection |
This configuration is required if you are using execution nodes to run OpenText Functional Testing tests. Without this configuration, test runs triggered by OpenText Core SDP remain Pending on Jenkins until someone logs in to the execution node either directly or with a remote desktop connection. To configure:
|
| Connect Jenkins to your OpenText Functional Testing machines |
To connect Jenkins:
For details, see the section on execution nodes in the Application Automation Tools wiki page. Note: If your Jenkins server is installed on a Windows machine, you can install OpenText Functional Testing on the same machine instead of creating execution nodes. |
|
Set up Jenkins to enable running OpenText Functional Testing API tests Relevant for: OpenText Functional Testing versions earlier than 14.01 |
To run API tests, you need the Script.dll and Script.pdb files that OpenText Functional Testing generates when it first runs the test. By default, these files are not stored in the SCM repository. To make these files available to OpenText Core SDP:
|
|
Set up Jenkins to enable opening OpenText Functional Testing tests result from OpenText Core SDP |
By default, Jenkins' Content-Security-Policy header prevents viewing OpenText Functional Testing test results reports remotely. To enable opening OpenText Functional Testing reports using the Show in Jenkins button in an automated test, you must clear the CSP property. Implement one of the following workarounds:
|
 Next steps:
Next steps: