Parameterize scripts
Use parameters in your scripts to enable the use of varying values rather than constant ones.
Overview
This topic describes parameterizing scripts, data-driving tests, and managing parameters.
Parameterize your script
When you parameterize a script, you replace constant values in the script with parameters. This enables you to do the following:
-
Re-use steps and create more flexible scripts.
-
Pass information from one step to another, by setting an output parameter in one step and using it as input for another step. This lets you perform actions based on your application's functionality.
-
Run the script multiple times, providing different data for each iteration. This data-driven testing lets you see how your application runs when different values are provided.
Data drive your test
When you create parameters, you can specify default values to replace them with during the run, if no other values are provided for the test run.
In codeless tests or MBT tests, you can create data sets, in which you specify parameter values to use when running the test. When you run your test with a data set, the script runs iteratively, using one row of parameter values from the data set for each iteration. For details on creating data sets and using them in your test runs, see Create a test suite with codeless tests.
Manage your parameters
Once a script is associated with a codeless test or a unit, the parameters are synchronized between the script and the test or unit. Any parameter names or default values added, modified, or removed in the Parameters tab of the test or unit are reflected in the Script parameters list, and vice versa.
If you save parameter changes in a codeless test or a unit while its script is open in FT Design, you see the changes in the script only if you reopen or reload the script. See also Managing changes from multiple sessions.
You can create input parameters and output parameters.
-
Use an input parameter to pass a value to a step's action or pass the text used to describe an object.
-
Use an output parameter to store the output value of a step or object to use later.
In a script, create and manage parameters in the Script parameters pane, and use them in your script steps:
Create script parameters
In the Script parameters pane, you can create, rename, and delete parameters. You can also define the default values to use for each input parameter. You can create parameters in advance, or while editing your script steps.
To create a parameter:
-
Open a codeless automation script.
-
Click the Script parameters button @.
The Script parameters pane opens.
-
Click + Create new.
The Add New Input/Output Parameter dialog box opens
-
Enter an unique parameter name. For input parameters, define a default value.
-
When you name a parameter, consider the following restrictions:
-
Case sensitive.
-
Must begin with a letter.
- Can contain only English letters, numbers, underscores ('_'), and dashes ('-').
-
-
Only String type parameter values are supported.
-
To manage parameters in the Script parameters pane:
-
To modify a parameter's name or value, hover over an input or output parameter and click the Edit button
.
When you change the name of a parameter, the parameter name is also changed in any steps that use this parameter.
-
To delete an input or output parameter, hover over a parameter and click the Delete button
.
Before deleting a parameter, make sure it is not in use by any steps. After deleting the parameter, any steps that use it are marked as incorrect.
Pass a value to the script
Use input parameters to pass external values to the script. You can use these values to define the script applications or in the script's steps.
You can also use parameters within the script, to pass values from one step to another.
-
Use parameters to define script applications: To dynamically describe the applications the script runs on, use parameters in the browser and URL fields of the script applications.
-
Pass a value to a step: You can use a parameter for an object's identification text, or for the step's input value. Therefore, the user interface presents the parameter options only for object classes that can be identified by text or for actions that accept input.
You can use an input or output parameter. When the script runs, the value of an input parameter is provided externally, from the data set. If an external value is not provided, the default value defined for the parameter is used.
If you use an output parameter, make sure a value is set into that parameter before the step that uses it as input.
Add the parameter to the step in the Editor, in the step editing pane, or during inspection.
To use a parameter to describe a script application:
-
Open a codeless automation script.
-
Open the script parameters pane.
-
Add a new application or edit an existing one.
-
Click the Use script parameter button
next to the Browser or URL input box.
-
In the parameter list, select an existing input parameter or click + New parameter to create a new one.
The browser or URL is replaced with the parameter and a dot on the parameter icon indicates that a parameter is in use.
When you run the script, any parameters you use in the application definition must have a valid value. This can be a default value, or a value provided by a data set.
The values for the browser field can be: Chrome, Edge, Firefox.
-
To switch to using a constant value, click the Use script parameter button
again and turn off the Use script parameter option.
To pass a value to a step in the Editor:
-
Open a codeless automation script.
-
Select the step in which you want to use a parameter.
-
Hover over the value or the object name in the step until the drop down arrow is displayed, then click the down arrow to open the parameter list.
Alternatively, you can type @ in the step line to open the list of parameters. Make sure to type the @ in a place in the step where it is relevant to insert a parameter.
-
In the parameter list, select an existing parameter or click + New parameter to create a new one.
The value or object name in the step is replaced with the selected parameter.
-
To switch to using a constant value, hover over the parameter, click its down arrow, and turn off the Use script parameter option.
To pass a value to a step in the step editing pane:
-
Open a codeless automation script.
-
Select the step in which you want to use a parameter.
-
Click the double arrow button
on the sidebar to display the step editing pane.
-
Click the Use script parameter button
next to the Identification text or Value input box.
-
In the parameter list, select an existing parameter or click + New parameter to create a new one.
The parameter is automatically added to the Identification text or Value input box and the step.
A dot is displayed on the parameter icon, indicating that a parameter is in use.
-
To switch to using a constant value, click the Use script parameter button
again and turn off the Use script parameter option.
To pass a value to a step during inspection:
-
Inspect your application or mockup images. For details, see Create steps by inspecting your application and Create steps by inspecting mockups.
-
Click a highlighted object. A pop-up dialog box with the suggested step and object description opens.
-
To use a parameter for the step's input value, click the Use script parameter button
next to the Value input box.
When inspecting a live application, you can use a parameter for an object's identification text:
-
Click Edit to open the Edit step pane.
-
Click the Settings button
 next to the Identification text, and select Use script parameter .
next to the Identification text, and select Use script parameter .
-
-
In the parameter list, select an existing parameter or click + New parameter to create a new one.
A dot is displayed on the parameter icon, indicating that a parameter is in use.
-
To switch to using a constant value, click the Use script parameter button
again and turn off the Use script parameter option.
Note: If you turn off a parameter in the Identification text box, the text reverts to the original value suggested by the inspection.
-
When the step is ready, add it to your test.
Store a value in an output parameter
You can pass a constant value, the value of an input parameter, or the value of an AI object into an output parameter.
| The value to pass | Step syntax |
|---|---|
| a constant value |
|
| the value of an input parameter |
|
| the value of an AI object |
Type one of the following syntax:
|
When you type @ in the step line after a Set command, a parameter list opens for you to select or create an output parameter:
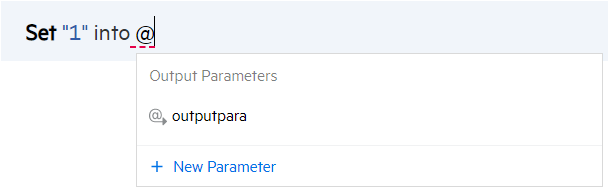
You can also hover over an empty line, click the Add step button 
Set "value" into @<output parameter name>
syntax.
To store the step result in an output parameter:
In the step editing pane, you can save the result of a conditional step or a verification step in an output parameter. For details, see Add conditional steps and Add verification steps.
 See also:
See also: