This section describes how to customize the criteria and the constant values used in risk-based quality management.
Overview
You use risk-based quality management to determine the Testing Level at which each requirement in the Requirements module is tested. For details about risk-based quality management, see Risk-based quality management.
You customize risk-based quality management to control the following.
| How to determine the Risk and Functional Complexity categories |
The Testing Level is determined by a requirement's Risk and Functional Complexity. Risk is comprised of the Business Criticality and Failure Probability. You determine values for these factors by assigning values to a series of criteria associated with each factor. Each criterion has a number of possible values. You can customize these criteria and values and how ALM uses them to determine the Business Criticality, Failure Probability, and Functional Complexity. |
| How to calculate Risk from the Business Criticality and Failure Probability | You can customize how Risk is calculated from the Business Criticality and Failure Probability. |
| How to define the default estimated Testing Time to test a requirement based on Risk and Functional Complexity | You can customize which Testing Time is associated by default with each Testing Level and Functional Complexity. In addition, you can customize how ALM determines the Testing Level with which to test a requirement based on the requirement's Risk and Functional Complexity. |
| Whether a requirement type enables risk-based quality management | See Customize requirement types. |
Customize criteria for Risk and Functional Complexity
You can customize the criteria used to determine the Risk and Functional Complexity of a requirement, the possible values for each criterion and the weight assigned to each value. You can then define how the total of these weights determines the Risk and Functional Complexity Categories.
To customize criteria, criterion values, and weights:
-
In the Project Customization window, in the left pane, click Risk-Based Quality Management.
-
Click one of the following tabs:
-
To customize criteria for determining Business Criticality, click the Business Criticality tab.
-
To customize criteria for determining Failure Probability, click the Failure Probability tab.
-
To customize criteria for determining Functional Complexity, click the Functional Complexity tab.
-
-
To add a new criterion, select the Criterion list and click New. Type a name for the criterion in the new row.
-
To add a description for a criterion, select the criterion from the Criterion list and type the description in the Descriptionof Criterion box.
This description is displayed in the Risk tab of the Requirements module when a user assesses Business Criticality, Failure Probability, and Functional Complexity. By providing a full description of each criterion, including an explanation of its available values, you help the user decide which value to assign to each criterion for a requirement.
-
To add a value for a criterion, select the criterion from the Criterion list and select the Value list. Click New. Enter a name for the value in the new row.
Note: Each value for a criterion must be unique.
-
To assign a weight to a criterion value, select the criterion from the Criterion list and then select the value from the Value list. In the Weight column for the value, Enter the weight to assign to the value.
When ALM calculates the Business Criticality, Failure Probability, or Functional Complexity of a requirement, it checks the values assigned to each criterion and calculates the sum of the corresponding weights for each value. This sum determines the Business Criticality, Failure Probability, or Functional Complexity. For details, see Customize weight boundaries.
-
You can delete a criterion or a value for a criterion:
-
To delete a criterion, select the criterion from the Criterion list and click Delete.
-
To delete a criterion's value, select the criterion from the Criterion list and the value from the Value list. Click Delete.
Note: Business Criticality, Failure Probability, and Functional Complexity must each have at least one associated criterion defined. In addition, each criterion must have at least one possible value.
-
-
To change the order in which criteria are displayed in the Criterion list, select a criterion and click Move Up or Move Down. Note that values for a criterion are automatically ordered by their weights.
-
Click Save to save your changes to the Risk-Based Quality Management page.
Customize risk calculations
You can define how ALM calculates the Risk value of an assessment requirement.
To customize risk calculations:
-
In the Project Customization window, in the left pane, click Risk-Based Quality Management.
-
Click the Risk Calculation tab.
-
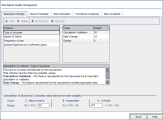
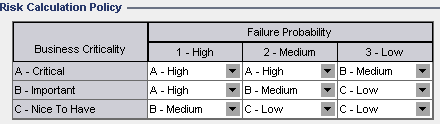
In the Risk Calculation Policy grid, you can define the Risk policy for testing a requirement.
To define Risk calculations based on Business Criticality and Failure Probability:
-
Click the arrow next to the cell in the grid corresponding to a particular Business Criticality and Failure Probability value.
-
Select a value.
The available values are A - High, B - Medium, and C - Low.
-
You can define the default estimated Testing Times required to test a requirement with each Functional Complexity value at each Testing Level. You can also define the default Testing Level used with each Risk and Functional Complexity Category. If a user does not enter different values for a requirement in the Requirements module, ALM uses these default values when calculating the estimated Testing Time for the requirement during the risk analysis.
Note: Modifying these criteria does not automatically affect the result of any existing risk analysis. To update the results of a risk analysis, you must perform the analysis again.
To customize risk-based quality management constants:
-
In the Project Customization window, in the left pane, click Risk-Based Quality Management.
-
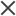
Click the Risk Constants tab. This tab displays constants used by default when calculating the Testing Time and Testing Level for a requirement.
-
In the Units used to measure Testing Effort field, select the unit of measurement that you want ALM to display when measuring Testing Time. The available units are Hours, Days, Weeks, and Months.
Note: If you change the units of measurement for a project, the Testing Time values are not updated automatically. For example, if the Testing Time of a requirement is 48 hours, and you change the units of measurement from Hours to Days, the Testing Time is still 48 days instead of 2 days.
-
Under Testing Time (full) per Functional Complexity, for each Functional Complexity value, type the estimated time required to fully test a requirement with the Functional Complexity value.
The Calculated Testing Time grid is updated to reflect these changes.
-
Under Testing level, in the Partial and Basic fields, enter the default Testing Time required for partial testing and basic testing of a requirement.
This should be expressed as a percentage of the time required for full testing. The Calculated Testing Time grid is updated to reflect these changes.
-
In the Default Testing Policy grid, define the default Testing Level for testing a requirement.
To define the default Testing Levels:
-
Click the arrow next to the cell in the grid corresponding to a particular Risk and Functional Complexity value.
-
Select a Testing Level from the available Testing Levels.
The available Testing Levels are Full, Partial, Basic, and None. Next to each Testing Level, you can see the estimated time needed to test a requirement at that level, based on the default Testing Times and Testing Levels you defined.
-
-
Click Save to save your changes to the Risk-Based Quality Management page.
 See also:
See also: