Use the Synchronize wizard
Use the Synchronize wizard to synchronize the changes in your work area with the Dimensions CM repository, update the work area, or deliver changes to the repository.
Synchronization overview
The Synchronize wizard enables you to review and compare the changes between files folders in your work area and repository. The wizard can make updates to the work area and/or a Dimensions CM project/stream based on this comparison, and critically provide easy resolutions to conflicts.
To resolve conflicts, Dimensions CM creates and maintains client metadata relating to the status of the item files. Dimensions CM creates the metadata for a file when you first get or check out the item to the work area. It subsequently updates the item when you synchronize or perform certain item operations such as check in or check out.
Note: Dimensions CM does not maintain metadata for directory items. The Synchronize wizard operations, such as deliver, update, and synchronize, may not work as expected for folder items.
Synchronization can be launched from any subfolder, acting recursively from that point. However, Dimensions CM makes the comparison relative to the root folder in the work area that corresponds to the top-level folder in the project/stream.
If you have made changes to the files or folders under the root folder, or someone has updated the items or folders in the project/stream, Dimensions CM can use this metadata to determine what changes were made, which file versions are the latest, and if any conflicts exist.
You can run the wizard from the Windows Explorer or from the project/stream in the desktop client. You can also launch the Synchronize wizard from Microsoft Visual Studio. For details, see Synchronize Dimensions CM projects.
Note: The Synchronize wizard runs on Windows platforms, but it can access files on Dimensions CM UNIX platforms that are referenced using the NODENAME:: or AREANAME:: syntax. The Synchronize wizard does not support MVS file systems.
Work with the Synchronize wizard
You can use the wizard with projects or streams:
| Projects |
|
| Streams |
For details, see Work with streams. |
When you run the Synchronize wizard, it compares the files and folders in the selected folder with the corresponding items and folders in the repository.
Synchronization example
In the following example, the folders in Windows Explorer are displayed with the corresponding project folders in Dimensions CM.
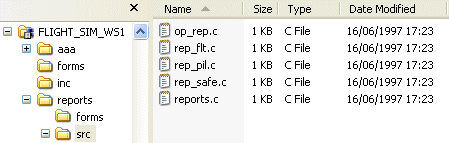
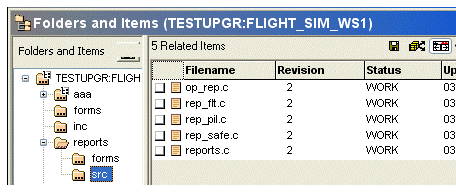
In the Synchronize wizard, the icons and the Change Type column tell you what the differences are.
When you select a file, the Synchronize wizard displays a more detailed description of the difference on the Properties tab, and the default action to take in the Resolution column. Use the toolbar buttons to select the action you want to take. The options for the selected file or folder are displayed on the Options tab.
Handle differences and conflicts
Typically, the Synchronize wizard can decide automatically what action to take when there are differences:
-
Deliver new files to the repository.
-
Update the work area with new item files.
-
Update the item files in the work area or repository with whichever are the latest versions.
-
Move or rename items in the repository to reflect any new name in the work area.
-
Move or rename items in the work area to reflect any new name in the repository.
-
Remove or delete items in the repository if they were deleted from the work area.
-
Delete items in the work area if they were removed or deleted from the repository.
Conflicts may happen when something has changed both in the work area and the repository. If there are conflicts, you need to decide which file version to use as the latest:
-
Ignore the conflict, leaving the versions in the work area and repository as they are.
-
Use the version in the work area.
-
Use the version in the repository.
If there is a conflict in the file content, use the merge tool to resolve the internal differences between the files. You can also set the Auto Merge option so that the file merge tool automatically resolves non-conflicting file content.
 See also:
See also: