Quality management
Monitor and measure product quality using the Quality module.
In this topic:
- Overview
- Shared application modules
- Build and maintain the application module tree
- Assign items to application modules
- Quality by application module
- Trace tests to application modules
- Track anomalies
Overview
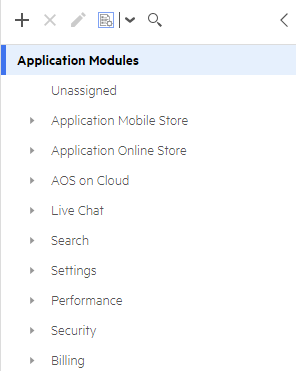
The Quality module is based on an application modules tree. The application modules tree is a logical depiction of the product, reflecting the product's functional areas. It is typically defined by the business analyst. The application modules tree shows how the application is broken down and allows you to track quality by logical business areas.
The Quality module includes tests, defects, and features, all of which can be associated with application modules to help you analyze quality by business areas, locate pain-points in your product, and concentrate your efforts in these areas. For details, see Assign items to application modules.
When deciding how to structure your application modules, focus on areas of the product for which you want to track quality, how you structure the application, and how users use the application.
Shared application modules
In workspaces that are members of shared spaces, you can create Shared Application Modules. Shared application modules are inherited by all workspaces in the shared space.
Users with space admin permissions can create or modify shared application modules.
Each workspace can add its own application modules to the shared application modules.
You can create shared application modules as top-level nodes, or as children of other shared application modules. For details on how to create shared application modules, see Build and maintain the application module tree.
Shared application modules can include custom fields that are defined at the shared space level. Workspace-specific custom fields are not available in shared application modules. In addition, team and user-type fields are not available in shared application modules.
In the Dashboard, you can create cross-workspace widgets that report on shared application modules.
Build and maintain the application module tree
Define your product areas as application modules.
To build the application module tree:
-
Open the Quality module.
-
In the application modules pane, click the Add item + button.
In shared space workspaces, shared space admins can create shared application modules. See Shared application modules.
-
In the Add Application Module dialog box, enter the required information.
If you selected an item in the tree, it is used as the parent item. You can drag items to rearrange the tree.
-
Repeat as necessary to create the full tree.
Building the application module is typically a process that requires a number of iterations. Drag and drop items to restructure the tree.
-
To display a subset of the application modules in the tree, click the Filter button. Choose whether to display only shared application modules, or selected application modules from the tree.
The root Application Modules node now aggregates only those items remaining in the filtered tree. This is reflected in the content included in the Overview, Tests, Features and Defects tabs when you select the root Application Modules node.
Assign items to application modules
Assign features, tests, and defects to application modules to help you assess product quality.
To find unassigned items, click Unassigned in the application modules tree.
To assign a single item:
Set the Application modules field in the item.
To assign multiple items:
- Open the relevant items' tab in the Backlog or Quality module, and select the required items.
- In the toolbar, click the Assign to Application Modules
 button.
button. -
In the dialog box, select the relevant application modules, and then click OK.
If you are assigning automated tests, click Assignment Rule to create a rule that assigns automated tests. For details, see To create test assignment rules from the Tests tab.
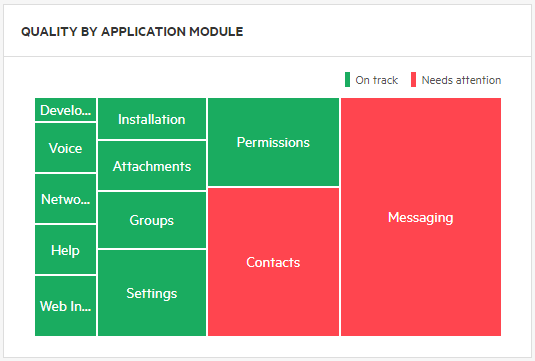
Quality by application module
Use the Quality by Application Module widget in the dashboard to see an overview of all application modules and identify those that need attention. You can configure the On track and Needs attention thresholds.
In the following example, the size of the application module in the widget is determined by the number of story points developed in the release and Needs attention is determined by critical open defects, low automation, or risky commits.
Trace tests to application modules
The following is a typical example of test traceability of a manual test.
- The backlog owner creates a new feature and assigns it to an application module.
- A tester creates a manual acceptance test for the feature (or one of its user stories) in the Backlog module. The test automatically inherits the feature’s application module.
- Access the test from the feature to understand feature coverage, and from the application module to understand the area coverage.
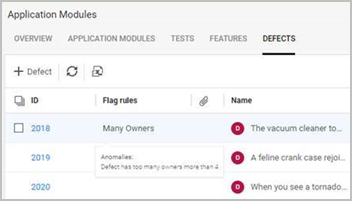
Track anomalies
When working with ALM Octane, it is useful to see anomalies in order to prevent delays in the development cycle. Examples of anomalies are defects stuck in one phase for a extended period of time, or a defect reassigned to many users.
Admins can define rules that flag anomalies within ALM Octane entities. For details, see Set up anomaly flags.
Once your admin has set up the anomaly flags, add the Flag rules column to your entity grid. It will show the anomaly if it is present. The tooltip shows details about the anomaly's threshold.
 Next steps:
Next steps: