The ALM Octane model
This topic describes the ALM Octane model, and how entities are hierarchically organized.
In this topic:
Overview
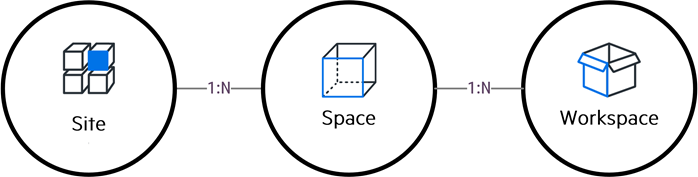
The ALM Octane model consists of:
-
A site, which contains spaces.
-
Spaces, which represent, for example, a business unit. Spaces contain workspaces and customization entities. For details, see Space/workspace overview.
-
Workspaces, which represent, for example, an application and its entities within the business unit—such as user stories, tests, and defects.
Every space has at least one active workspace, the default workspace. The original name of this workspace is default_workspace. It can be renamed, but cannot be deleted.
Entities and their contexts
The model operates on these levels, Site (on-premises), space, and workspace. These contexts are also the entry points into the REST API. Every entity exists in one of these contexts.
| Entity type | Description |
|---|---|
| Shared |
To facilitate sharing between workspaces, ALM Octane stores shared entities in a shared_data resource. Shared entities stored here are available to all associated workspaces. Shared entities include items like rules, user-defined lists, and releases. |
| Non-shared |
Entities that are not shared are stored in each individual workspace. |
| Space |
Space entities are entities that are defined at the space level, regardless of whether the space is shared or isolated. These entities include users, API keys, and more. These entities are available from the space context. |
Note: Unless indicated otherwise, the documentation and examples in this ALM Octane Developer Help assume the context of workspaces in an isolated space.
For details, see Entry points and their contexts.
 See also:
See also: