Auditing entities (technical preview)
Site and space admins can view changes made to entities using the audits resource. Using this resource you can monitor enterprise-readiness, such as viewing regulatory activities, such as security and GDPR compliance.
Overview
Use the audits resource to view activities that relate to GDPR compliance and security regulations. This resource retrieving more audit information than is available in the History tabs in the ALM Octane user interface.
The audits resources is not entity-based, so you can audit across multiple entities.
Site and space admins can audit entities on the site, space, and workspace levels, assuming the following:
-
The admin has the appropriate roles and permissions for the contexts.
-
Auditing is supported for the relevant entities. To determine which entities can be audited, see the non-auditable feature under Entity metadata reference.
This resource is available to all site and space admins, even those with data access restrictions.
ALM Octane supports auditing of the following operations: Create, Update, and Delete.
Note: As a technical preview, this resource is subject to change.
To prevent retrieving huge numbers of records the resource is limited by default to 10,000 records. This limit can be lowered using the configuration parameter MAX_LIMIT_ELASTIC. The limit cannot be raised.
URIs
Depending on the context, the URIs for auditing are as follows:
Adding queries to audit requests
We add queries to filter how much information is returned by the audit. The following clauses are available:
-
How the returned data are paged. See Page data (limit, offset, total_count).
-
Retrieving only the fields you need by using a fields clause. See Select fields (fields)
-
Filtering the instances to be returned with a query clause. See Query.
Caution: If no query is supplied, all operations for all entities are returned. Therefore, for performance, we recommend that you always add a query clause to the request.
Use a semicolon to separate the clauses in the query. This represents the And relational operator.
You can query on the following items:
| Query item | Description |
|---|---|
|
entity_type |
You can audit by entity type, such as teams, features, or pipelines. Configuration parameters: To audit configuration parameters, use the following entity type name: To see the entities you can audit, see the non-auditable feature under Entity metadata reference. |
|
entity_id |
You can audit by the ID of the entity. |
|
field_name |
You can audit changes made to a specific field of an entity. To see which fields are available, see the non-auditable feature under Field metadata reference. |
|
action |
You can audit the following actions:
|
|
user_id |
You can request the changes made by a specific user. Enter the user ID without quotes, as user IDs are integers. Note: Every user in ALM Octane has two IDs. If you are on the auditing on the site level, specify the site user ID. If you are auditing on the space or workspace level, make sure to specify the space user ID. |
Example: This query indicates that we are auditing all the updates that user 8987 made to the Severity field of the story whose ID is 2004: ?query="entity_type=^story^;entity_id=2004;field_name=^severity^;action=^update^;user_id=8987"
Examples
Here are some examples for working with the audits resource.
Auditing deletions made during a specific time frame
This example demonstrates how to see all the entities that were deleted since the beginning of the year 2019.
Auditing a workspace-level entity at various stages
In this example, a workspace admin audits an epic with ID 1125. The response shows its creation, updates made to the epic, and its deletion.
Note: It is not enough to specify the entity_id. There may be other entity types, such as user stories or features, with the same entity ID. Therefore, make sure to also specify the type of the entity.
Request:
Response:
This collapsed JSON representation shows that the entity underwent three actions. The most recent operation is always at the top and labeled 0.
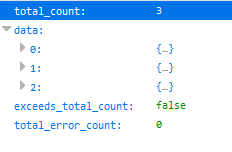
Note: If a rule made a change that is displayed in the audit, the following is displayed in the response:
"rule_changer_id": <rule ID>
This is in addition to the user_id who ran the rule.
Action 2 is the creation of the entity. The action is "create." Each field that received a value during the create is listed in the change_set attribute.
{
"type": "audit",
"workspace_id": 1002,
"entity_physical_id": 1125,
"change_set": [
{
"field_type": "SINGLE_REF",
"field_name": "author",
"value": "1001",
"value_id": 1001,
"ref_entity_type": "workspace_user",
"field_label": "Author",
"value_text": "marta@thecompany.com"
},
{
"field_type": "STANDARD",
"field_name": "logical_name",
"value": "qdk3no4m41kvzs9w5lkdrjv94",
"field_label": "Logical name"
},
{
"field_type": "STANDARD",
"field_name": "name",
"value": "Epic 1",
"field_label": "Name"
},
{
"field_type": "SINGLE_REF",
"field_name": "parent",
"value": "1001",
"value_id": 1001,
"ref_entity_type": "work_item",
"field_label": "Parent",
"value_text": "Backlog"
},
{
"field_type": "STANDARD",
"field_name": "path",
"value": "0000000000Z3",
"field_label": "Path"
},
{
"field_type": "SINGLE_REF",
"field_name": "phase",
"value": "phase.epic.new",
"value_id": 1019,
"ref_entity_type": "phase",
"field_label": "Phase",
"value_text": "New"
},
{
"field_type": "STANDARD",
"field_name": "subtype",
"value": "epic",
"field_label": "Type"
}
],
"entity_type": "epic",
"user_id": 1001,
"user_name": "marta@thecompany.com",
"action": "create",
"session_id": "$1$XHYKNW1C$IhyU1Zzj7N0rlfLwoeWGQ0",
"entity_id": "1125",
"timestamp": "2018-12-13T11:18:42Z"
}
Action 1 is the update of the entity. The action is "update." Each field that was updated is listed in the change_set attribute. Fields receiving values for the first time during the update are listed with their current value. For fields whose values were modified, both the old and the current values are listed.
{
"type": "audit",
"workspace_id": 1002,
"entity_physical_id": 1125,
"change_set": [
{
"field_type": "MEMO",
"field_name": "description",
"value": "<html><body>\n<p>Adding a description to my epic.</p>\n</body></html>",
"field_label": "Description"
},
{
"field_type": "SINGLE_REF",
"field_name": "epic_type",
"value": "list_node.epic_type.Business",
"value_id": 1035,
"ref_entity_type": "list_node",
"field_label": "Epic type",
"value_text": "Business"
},
{
"field_type": "SINGLE_REF",
"field_name": "item_origin",
"value": "list_node.item_origin.alm",
"value_id": 1051,
"ref_entity_type": "list_node",
"field_label": "Item origin",
"value_text": "ALM"
},
{
"field_type": "SINGLE_REF",
"field_name": "owner",
"value": "1001",
"value_id": 1001,
"ref_entity_type": "workspace_user",
"field_label": "Owner",
"value_text": "marta@thecompany.com"
},
{
"field_type": "SINGLE_REF",
"field_name": "phase",
"value": "phase.epic.inprogress",
"value_id": 1020,
"old_value_id": 1019,
"ref_entity_type": "phase",
"old_value": "phase.epic.new",
"field_label": "Phase",
"value_text": "In Progress",
"old_value_text": "New"
},
{
"field_type": "STANDARD",
"field_name": "story_points",
"value": "10",
"field_label": "Story points"
}
],
"entity_type": "epic",
"user_id": 1001,
"user_name": "marta@thecompany.com",
"action": "update",
"session_id": "$1$4YoRwEtz$/72LHp9E93e2.WoC8uQjh0",
"entity_id": "1125",
"timestamp": "2018-12-13T11:38:05Z"
},
Action 0 is the deletion of the entity. The action is "delete."
{
"type": "audit",
"workspace_id": 1002,
"entity_physical_id": 1125,
"change_set": []
"entity_type": "epic",
"user_id": 1001,
"user_name": "marta@thecompany.com",
"action": "delete",
"session_id": "$1$4YoRwEtz$/72LHp9E93e2.WoC8uQjh0",
"entity_id": "1125",
"timestamp": "2018-12-13T11:38:05Z"
},
Auditing a release, which is a "shared_area" space-level entity common to all workspaces
In this example, a workspace admin audits a release with ID 1001.
The shared_area context is a special area in a space that contains shared assets.
Auditing a workspace, which is a shared, space-level entity
In this example, a space admin audits all operations on all workspaces.
Auditing a specific user's activities
This example demonstrates how to get the history for all the actions performed by user 2002, Marta Santora.
Auditing multiple attributes
This example demonstrates how to audit all updates that user 8987 made to the Severity field of the story whose ID is 2004:
 See also:
See also: