Quality risk analytics
Quality risk analytics aims to help you identify areas in your product with high quality risk, and reduce the risk in those areas.
Overview
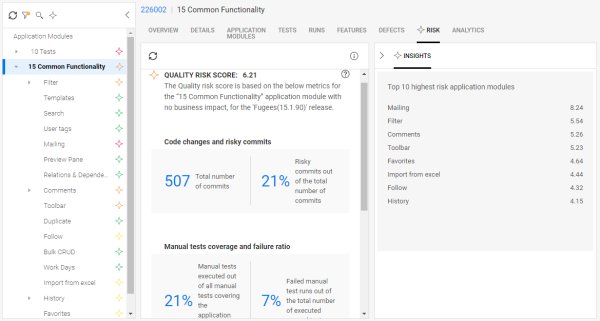
The quality risk insights present scores to help you identify the problematic areas.
The risk scores are based on the selected timeline of the selected release. A risk baseline is calculated from within all of your application module nodes. The problematic nodes are then compared with the baseline, and a risk index is calculated.
Depending on the risk score, a set of tests are provided that can help reduce the quality risk.
Risk factors
The following table lists factors that are analyzed to determine if an item is high risk.
Apart from the risk factors below, the application module's business impact is also considered as part of the module's quality risk score. For details, see Business impact.
| Risk factor | Detail | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Code changes | There were recent code changes in this area and many commits. Risky commits can impact the risk level of your product. For more details, see Identify risky commits and features at risk. |
|
| Test coverage | An area was not sufficiently tested during the selected period. This is indicated by a low percentage of executed tests out of all tests covering that area, since the changes were introduced. |
|
| High failure ratio | There was a high failure rate of manual tests in a specific area, which may indicate instability and a low quality area. A high number of test failures can indicate that issues or defects were found. |
|
Note: Each of the risk factors has a relative weight in calculating the risk score. If you want to change their default weights, adjust the values of the following configuration parameters: QUALITY_RISK_COMMITS_PERCENT, QUALITY_RISK_FAILED_MANUAL_PERCENT, QUALITY_RISK_RISKY_COMMITS_PERCENT, QUALITY_RISK_TEST_COVERAGE_PERCENT.
The total of the parameter values should equal 100.
Quality risk analytics benefits
With quality risk analytics, you can identify areas in your product with high quality risk. Once identified, you can run the recommended tests to reduce the risk. This helps increase the efficiency of your testing strategy and minimize defect leakage to production.
When planning a release, dev leads and QA stakeholders need to address the following questions:
- How should I define my testing strategy?
- Which areas are in high quality risk?
- Where might there be a high probability of detecting defects with a high business impact?
- Where should we focus testing during the current sprint or release?
- How can I conserve time by not testing relatively good quality areas?
Quality risk insights provide quantifiable metrics for the risks in your application modules.
The color-coded star icons in the Application Module tree provide immediate visibility to the risk level. For details, see Application module risk indicators.
Interpret the analytics
To open the quality risk insights, in the Quality module, select an application module from the application modules tree, and then select the Risk tab.
The quality risk insights page consists of three panes:
- Application modules tree with risk indicators
- Details on the selected module's quality risk index and metrics
- Insights sidebar showing top ten application modules with the highest risk
Application module risk indicators
In the application modules tree, a colored risk indicator is assigned to each module to indicate its risk level.
The risk level and indicator are determined by the node's overall score. Hover over a risk indicator to see the module's risk level and score.
| Risk level | Risk score |
|---|---|
 Low Low |
0.1- 3.9 |
 Medium Medium |
4.0 - 4.9 |
 High High |
5.0 - 6.9 |
 Critical Critical |
7.0 - 10.0 |
Note: The lowest quality risk score is 0.1, even when risk levels are negligible.
Quality risk index and metrics
The main pane lists the overall risk score and the metrics that were used to calculate the score. The higher the overall score, the higher the risk.
The quality risk metrics are quantifiable numbers that allow you to drill down to the problematic areas. The metrics are divided into the following sections:
| Section name | Factors for the selected application module node |
|---|---|
| Code changes and risky commits |
|
| Manual tests coverage and failure ratio |
|
| Automated tests coverage |
|
Top ten highest risk application modules
The Insights sidebar lists the sub-modules of the selected application module, with the top ten highest risk scores.
The quality risk score is calculated automatically every few hours based on the data shown in the main pane, such as your application module's code changes and test coverage. A higher score indicates greater risk.
For details, see Quality risk insights.
Business impact
When calculating the quality risk of your application modules, it's important to assign the correct business impact according to your business decisions. If you have an application module that is high risk due to many code changes and low coverage, but its impact on your business is low, then the quality risk score decreases. Alternatively, if you have an application module with few code changes, but with a high business impact, then the quality risk score increases.
Your product’s business analyst, QA lead, or similar stakeholder should indicate the business priorities by assigning a value to the Business impact field for each application module. The business impact value is used in the calculation of the quality risk score and metrics.
To set a Business impact value, open the Details tab and select a value from the list. For new application modules, for newly created shared spaces, the Business impact field is mandatory.
The quality risk is based on two primary factors: the calculated score for the probability of hidden defects and the business impact. The following table describes the effect of the Business impact setting on the quality risk score.
| Business Impact field options | Impact on quality risk score |
|---|---|
| Low | Reduces the score, even if there is a high probability of hidden defects. |
| No Impact | Has no effect on the quality risk score. |
| Medium | Slightly increases the quality risk score. |
| High | Moderately increases the quality risk score. |
| Critical | Substantially increases the quality risk score. |
Note:
-
The quality risk score and metrics are recalculated using these settings every six hours.
-
You may encounter inconsistencies between the business impact and real time data. This is a result of a lag in updating data. The data is only current for the last time the quality risk was calculated.
-
This setting can also be changed using the QUALITY_RISK_BUSINESS_IMPACT configuration parameter.
Set up the quality risk calculations
After you build your Application Modules tree and run tests, risk analysis insights can be generated.
Note: Before risk scores are calculated, make sure that your business analyst has set the Business Impact field in the application module's node. If it is not set, the risk is calculated only according to the metrics that indicate a high probability of detecting defects in a certain area. For details, see Business impact.
To enable the quality risk calculation:
- Select the Risk page under the Quality module.
- In the Application Modules tree toolbar, click the Quality Risk Settings button
 .
. - The Show quality risk indicators option is activated by default, allowing quality risk metrics to be calculated. You can deactivate risk calculation if the insights are not relevant to you.
- From the Release dropdown, select the release for which to calculate values.
-
In the Filter section, select the test types or levels to include in the calculation.
You should only include tests that impact the quality of your release and that were relevant at the time of the release. If new tests were added for the application module that are relevant for an upcoming release, you should consider filtering them out so that they won't affect the score.
To increase the accuracy of the analytics, consider the following common filters.
Test type Recommendation Automated Tests Set the Test level to System Test and Functional Test level, but exclude Unit Test. Manual Tests Set the Test type to End to End, Sanity, and Regression, but exclude Acceptance tests. Note:
- Filters on tests are set per release and not per user. Setting these filters requires Set quality risk configuration permissions in the Application Modules category. By default, only workspace admins have this permission.
- The Program filter is not applied to the risk calculation.
-
Click OK. The risk scores are calculated.
Select an application module's root node to display the quality risk score and metrics of all its application modules. The metrics are averaged together to give an overall quality risk score.
Only medium and high-risk modules are displayed in the Top 10 list.
Perform risk-based testing
Quality risk analytics helps minimize your testing effort by recommending a set of tests to run on high-risk areas that may have hidden defects. It also helps increase your certainty about the quality of application modules with high quality risk scores.
The quality risk analytics aims to provide the minimum number of tests per area with the highest potential to find defects. By default, up to 30 tests can be recommended, depending on an application module's risk score.
- Note:
- Your admin can change the maximum number of recommended tests by modifying the LIMIT_TESTS_IN_RECOMMENDED_GRID parameter. For details, see Configuration parameters.
- The Reduce risk option is not available for modules with low risk scores. You should focus your testing effort on high-risk areas.
Criteria for recommending tests
The history of test runs is reviewed to learn which tests are more effective at a certain point in time.
The main criteria for recommending tests are based on the quality score of the area the test covers, the test's failure ratio, and the time of its last run.
Whether a test is recommended depends on the following indicators.
| Recommended | Details |
|---|---|
| Yes |
A test is recommended if:
|
| No |
A test is not recommended if:
|
For details on risk-based testing insights, see Quality risk insights.
Tests are recommended based on their priority, starting with most recommended.
The test priority is determined by the following metrics.
| Metrics | Details |
|---|---|
| Application module risk score |
A test covering an application module with a high-risk score has priority over tests that cover an application module with a lower risk score. If several tests cover the same application module with a high-risk score, their priority is determined by the tests' failure ratio. |
| Test failure ratio |
The history of all tests covering the selected application module and its top high-risk child modules are reviewed, and the tests with the highest percentage of failed runs are identified. The tests with the highest failure ratio is listed first. A high failure ratio indicates that the test is more likely to find hidden defects, and thus is more effective. Note:
|
For details on the recommended tests insights, see Insight cards.
Quality risk score for a specific application module reflects the level of uncertainty about the module's quality. Risk-based testing helps you reduce this uncertainty represented by the module's high-risk score.
To perform a risk-based testing:
-
In the Application Modules tree, select a high-risk application module.
If you do not select a specific application module, tests are recommended that cover one of the top 10 modules with the highest risk scores.
-
On the Risk tab, in the Insights pane, click Reduce Risk.
A grid with recommended tests is displayed.
Tip: You can filter the list of recommended tests in the Quality Risk Settings
 .
. -
In the Recommended tests to reduce quality risk dialog box, select the tests to run.
Step Details Select all the recommended tests Up to 30 tests can be recommended, depending on the application module's risk score.
Running all the recommended tests can be time consuming.
Select specific tests You can select only specific tests which you consider most effective in detecting defects and reducing quality risk.
Tip: When selecting tests to run, consider the tests' priority in the Recommendation order column.
- Add tests to an existing test suite or create a new test suite.
- Go to the Tests tab, and run the recently created or edited test suite.
By running the given test suite, you become more certain about the application module’s quality. Regardless of the suite run results, the quality risk of the given area is immediately reduced due to the additional coverage.
Adjust your testing strategy
Based on the risk index and scores, you can devise a more effective testing strategy. Suggested strategies may include:
- Increasing test coverage in the problematic areas.
- Concentrating on the risky areas and minimizing efforts in the low risk areas.
- Understanding why the number of defects was high.
- Determining why there was a high failure rate for the tests.
 See also:
See also: