Models
Create a model to represent your application’s business processes. After creating the model, you choose paths in the model to test based on your testing strategy.
Create a model manually
You can create a model using units you have already defined, or using placeholders that you later replace with or convert into units. You can also include a model as a sub-model, inside a larger model.
Tip: You can also import a BPMN file to inject its model into MBT. For details, see Import a BPMN file.
To create a model:
-
Select a folder or create a new folder. This structure enables you to organize your MBT models in a way that is meaningful to you.
-
In the Models tab, click + Model.
-
Enter the model's name, and fill any other fields that are relevant.
-
Click a model's ID to open it for editing.
Build a model using the components in the side pane, and the toolbar in the model editor pane. For details, see Build and edit a model.
Generate a model with Aviator
Requires an  Aviator license
Aviator license
Leverage Aviator’s Generative AI capabilities to generate a model automatically from a feature description. You can provide the description in one of the following ways:
-
Enter a feature description directly in the model-generating dialog box.
-
Select an existing Feature entity to use a basis for the model. In this case, you can choose to include feature attachments, user stories, and comments when generating the model.
Make sure the feature description is as detailed as possible. Specify the complete business flow, including details such as functionality, exceptions, and error handling. The quality of the description affects the accuracy and detail of the generated model.
The generated model includes a diagram containing placeholders. The placeholder name describes the step it performs in the flow. In addition, each placeholder includes a Description and an Expected result. To see the details of a placeholder, hover over the placeholder's information icon ![]() .
.
The generation process is iterative. First, a model suggestion is generated. You can save this suggestion as a Model, or create additional drafts, adjusting your feature description and context, until you are satisfied with the suggested model.
This section includes:
Generating parameterized placeholders
To generate a model suggestion:
To refine the generated suggestion:
To save a suggested draft as a model:
To open and review the generated model:
Generating parameterized placeholders
When generating a model, you can select to generate parameterized placeholders. In this case, the generated placeholders include parameters for details that might differ between test runs or iterations. For example, a log in placeholder would use parameters for the username and password.
The model might also include additional paths based on different expected parameter values. For example, if your model includes a login step that requires registration before the first login, an account_exists parameter might be included in the login placeholder. The model would have one path for logging in right away if an account exists, and another for registering first if it does not.
Including parameters in your generated model introduces data driving into your process from the outset. When you run your MBT tests, you can provide different values for these parameters for different runs or iterations.
You can generate a model with and without parameters and compare the two before you decide which model to use.
Note: When you convert the placeholders into units, the corresponding unit parameters are created, without default values.
To generate a model suggestion:
-
In the Model-Based Testing module, open the Models tab and click
 Generate an MBT Model.
Generate an MBT Model.The Generate Model-Based Testing Model window opens.
-
Select whether to generate the model based on a description you enter or based on an existing feature:
-
Custom description. Enter a description of your feature. You can copy it from a design document, or write a new description.
-
Based on a Feature. Click in the rectangle that opens to select a feature from the backlog. The feature's description is displayed.
Tip: You can get to this point from a Feature entity, by opening the Aviator pane and clicking the Generate an MBT Model power action, or selecting the Details tab and then clicking More >
 Generate an MBT Model.
Generate an MBT Model. Review the description and make any adjustments needed. The changes you make are used for the model generation but are not saved to the Feature's description.
-
-
(Optional, relevant for Based on a feature) Select additional context to include in the Model generation:
-
Click Select Feature attachments or Select User Stories related to the Feature.
The relevant feature assets are displayed for selection.
-
Select whether to Include Feature comments.
-
-
(Optional) Provide additional guidelines to consider when generating the model suggestion. For example, terminology to use, use cases to consider, or technical constraints.
-
(Optional) Select Generate parameterized placeholders. For details, see Generating parameterized placeholders.
-
Click Generate. A read-only model suggestion diagram is generated. The model's flows are verbally described in a Reasoning tab added near the Model Description.
To refine the generated suggestion:
You can restart or fine-tune your feature description and context and repeat the generation process to create a new model suggestion.
-
In a Draft tab containing a suggested model, do one of the following:
-
To create an editable copy of the current description and context, click Duplicate and edit description.
A new Draft tab opens containing the same description and selected options.
-
To start anew, click the + icon in the Draft tab strip.
If the suggested model was based on a custom description, an empty Draft tab opens
If it was based on an exiting feature, the new Draft tab contains the original feature's description.
The previous Draft tab becomes read-only.
-
-
Refine the description or change context selections as needed.
Tip: You can use the Reasoning tab, or compare the Reasoning tabs of multiple models to help refine your description or decide what options to change.
If you click Discard, all the changes you made in this draft since its creation are discarded.
-
Click Generate to generate a new suggested model.
Notes on working with Drafts:
-
You can edit or generate new drafts only from the right-most tab.
-
You can go back to earlier tabs, view their content, close them, or save their suggestions as new models.
-
Up to 10 drafts can be open at one time.
To save a suggested draft as a model:
-
Select the Draft tab containing the suggestion you want to save.
-
Click Save this draft as Model.
A new Model entity is created. If you generated the model based on an existing Feature entity, the new Model entity is related to the Feature.
When the generated model is ready, a notification is displayed, containing a link to the new model. A link to the new model is also added to Draft tab that generated the model.
To open and review the generated model:
The new model is stored in a folder named Created by Aviator. Click the model's ID to open the model and view its diagram and placeholders.
Tip: If you open a model from its link while the model generation wizard is open, the model opens in a new browser tab, keeping the wizard open in the original browser tab.
An AI-generated model may be inaccurate and incomplete. Make sure to review the model carefully before you continue to work with it.
If necessary, adjust and edit the model's diagram using the tools described in Build and edit a model.
Build and edit a model
-
From the components pane, drag and drop units or models into the model diagram.
Use the filter and search buttons at the top of the components pane to locate components.
Note: When you open a model in the model editor, the units included in the components pane are filtered by default. Unless you modify this filter, only units that are directly related to the model’s branch in the hierarchy are displayed, and not all of the units in the workspace.
If you modify this filter, your new settings will override the default branch filter until the filter is completely cleared.
-
Drag and drop elements from the floating toolbar:
Tool Description Placeholder
Temporary element to reserve a space for another component.
Drag and drop a placeholder in the model diagram. Later, you can drag an element from the components pane onto the placeholder to replace it. Alternatively, use a placeholder's right-click menu to convert it to a unit.
This can be useful if you want to first build a theoretical model, and then create corresponding units.
Note: If the placeholder was created by Aviator and contains parameters, the corresponding unit parameters are created without default values.
New unit
Drag and drop into the diagram to create a new unit. For details, see Units.
The unit is then added to the components pane.
Note: If the placeholder was created by Aviator and contains parameters, the corresponding unit parameters are created without default values.
Comment
Add a note to the diagram.
-
You can drop a comment element in an empty space to create a general note on the model. This is not connected to a specific element in the diagram.
-
You can also drop a comment onto a specific unit or model in the diagram. A comment icon appears on the element, and you can hide or show the comment. If you move the element, its comment moves with it.
Decision point
A decision point can have multiple inputs and outputs, and is used to build optional process flows.

End point
A model can have a single or multiple end points.
You can right-click an End point to convert it into a Terminate point
 (and vice versa).
(and vice versa).A termination point specifies a point in the business process where the flow should immediately terminate. This is useful, for example, when you don't want the flow to continue in a parent model once the child model ended.
Note: To add an endpoint to a sub-model, you need to open the sub-model for editing. You cannot drag an end point into a sub-model when it is in the context of the model.
-
-
Nested models: You can nest a model inside a model. In this case you can expand the sub-model to see its contents, but they are read-only. To edit the sub-model, open it from the components pane.
You can also nest a sub-model inside another sub-model, but you cannot expand the nested sub-model.
-
Within a model diagram, you can use the following actions:
-
Zoom in or out of the diagram using the controls in the corner.
-
Activate Pan or Selection mode by clicking the Pan mode button
 and the Selection mode button
and the Selection mode button  in the floating toolbar.
in the floating toolbar. -
Undo or redo actions by clicking the Undo button
 or the Redo button
or the Redo button  in the floating toolbar.
in the floating toolbar. -
Cut, copy or delete elements using their right-click menu commands.
The Start element is permanent and cannot be removed or copied.
-
If you select multiple items, you can select More > Bulk Update in the toolbar to update their shared properties.
-
-
After placing tools and components on the diagram, click and drag from the edge of one element to another to connect them.
-
Use the buttons above the diagram to Save changes, Discard changes, or Refresh the model using the last-saved display.
Use the Grid option to apply a grid to the model for visual purposes.
Click the Apply layout button
 to automatically organize the model in a structured display.
to automatically organize the model in a structured display.
After saving a model, you can select it in the Models tab and view its diagram in the side pane.
To generate a JPG image of your model that can be shared, click the Export as image button  .
.
Replace placeholders with units
To replace a placeholder in a model diagram with a unit, you can drag an existing unit onto the placeholder or convert the placeholder into a unit. You can also convert all placeholders in a model to units at once.
To convert a placeholder into a unit:
-
In a model's diagram, right-click a placeholder and click Convert to Unit. A new unit opens.
The placeholder's name is used for the name of the new unit.
If the placeholder was created by Aviator and contains a Description and Expected result, these are included in the unit's Description.
-
Accept or edit the unit's details.
-
Click Add.
To convert all placeholders in a model into units:
If a model contains placeholders, the model's diagram toolbar includes the Convert all to units button.
-
Click Convert all to units.
-
In the confirmation dialog box that opens, click Convert.
Note: Placeholders in sub-models are not converted.
All of the placeholders in the model are replaced with the relevant units:
-
The placeholder's names are used for the names of the new units.
If the model contains multiple placeholders with the same name, only one unit is created with this name. The same unit is used to replace all relevant placeholders in the model diagram.
-
If a placeholder was created by Aviator and contains a Description and Expected result, these are included in the unit's Description.
If there are multiple placeholders with the same name and one or more of these placeholders contain a Description and Expected result, the new unit created with this name is given the information from one of the placeholders.
Add relations to a model
You can create requirements and features, and then link models to those entities. This can help ensure that new features or requirements are properly covered in testing.
Relations are automatically created between models or units and their tests.
To add relations to a model:
-
Create requirements or features using the Requirements module.
-
In the Models tab, open a model.
-
In the Relations tab, create relations between the model and its related requirements or features.
Relations between models or units and a test are created automatically when you generate the test. In addition, if you add a sub-model or unit to a model with related tests, the tests are automatically related to the new unit or sub-model.
Example: The model Card selection is a sub-model in the New bank customer model. It is covered by two tests, and related to one feature and one requirement.
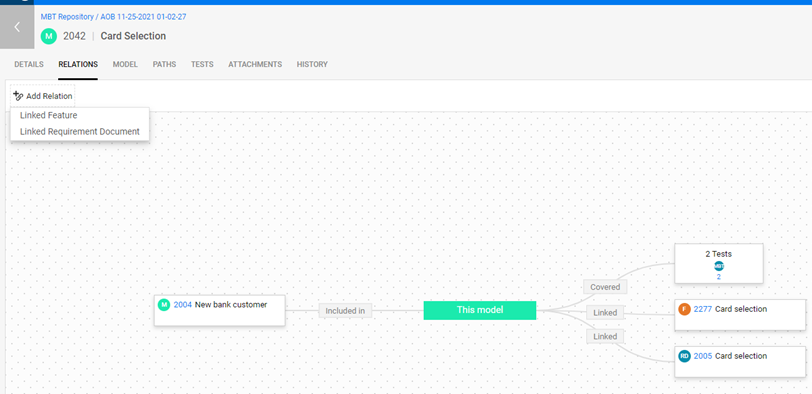
Modify a model's details and phases
You can add the following details to your model In the Details tab:
-
Define further information such as adding tags to a model, assigning a model to your My Work area, or working with custom fields.
-
Assign a model to an application module, indicating the area of your application that this model is related to.
You can assign the model in the Details pane, by setting its Application Modules field, or in the Quality module, by dragging the model from the Model Items tab onto the Application modules pane.
Similarly, you can assign MBT tests and units to application modules as well. Note that MBT tests are displayed in the Quality module in the Tests tab.
-
Set the model's Phase. MBT uses phases to represent the current state of an item. As you work on items, advance them from phase to phase. When you set a model's phase to Ready, the icon representing the model changes color.
View a model's hierarchy
In a Model entity's Details tab, click the View Model hierarchy button. The Model hierarchy displays the following:
-
A multi-level list of all the sub-models contained (nested) under this model.
-
A single-level list of the models in which this model is contained (nested) as a sub-model.
Tip: You can select one or more items in the list and then copy their links.
View a unit's summary
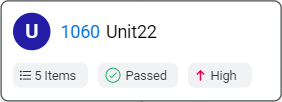
Unit cards display summary information in the context of the models and testing paths.
-
In the Models tab, unit cards include details on related backlog items, latest run results, and risk. Tooltips show additional information where relevant.
-
In the Paths tab, units in the Path Preview pane display information related to your strategy. If you select the Agile Based strategy, you see details on related items. If you select Unit Recent Failure strategy, you see latest run results.
Export and import a model across workspaces
You can export one or more models from a workspace, and import them to another workspace.
Before importing a model, we recommend that you configure an MBT runner in the new workspace that is associated with the Git repository you want to work with. If you do not configure a runner before importing, you will need to manually update the relation of each of the units in the new workspace with the Git repository.
To export a model:
-
In the Models tab, select one or more models for export.
-
In the More menu, select Export to JSON and save the export file.
To import a model:
-
In the target workspace, open the Settings menu
 and select Import > Model Items.
and select Import > Model Items. -
Select JSON and browse to the saved file.
Note: If you want to run tests automatically, you must have an MBT runner configured in the workspace that is associated with the Git repository.
-
Click Import.
The model is imported to the new workspace.
 See also:
See also: