Relationships between objects
Relationships provide traceability between items, design parts, and requests. This topic describes the types of relationships between Dimensions CM objects.
About object relationships
Relationships between objects determine how the objects may impact each other.
You can use relationships to record whether an item is affected by an issue reported in a request, or to specify other items which are derived from, or which are used to derive, an item.
Relationship types are system-defined or user-defined.
If you are the Product Manager, you can set up user-defined relationship types in the Administration Console. For details, see Assign valid relationships.
Item-design part relationships
Items are related to design parts to establish where an item belongs and where it is used within the product.
An item is either owned or used by a design part. Only one design part can own an item, but several design parts can use it.
Item-design part relationships apply to all revisions of the item.
Item-design part relationships are:
| Relationship | Description |
|---|---|
| Owned | A single design part can own any number of items. This relationship indicates the part of the product in which the item belongs. |
| Used | An item can be used by any number of design parts. This relationship indicates that the item is reused in different parts of the product. |
The item Logo.gif, which is the company logo bitmap in the product Sales, is owned by the design part Docs and is also used by design part GUI.
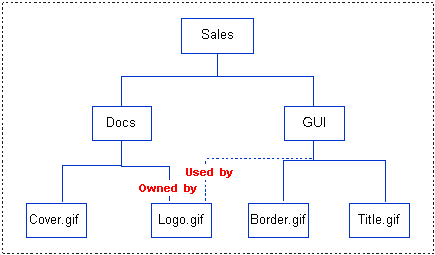
Item-item relationships
Use item-item relationships to show a dependency or connection between an item and other items.
Items can be related to one another by system-defined or user-defined relationships. The system-defined relationships are determined by your process model and cannot be changed.
System-defined item-item relationships are:
| Relationship | Description |
|---|---|
| Made Of | An item is made of those item revisions from which it was created by a build process. |
| Made Into | An item is made into those item revisions that are built from it. |
| Created From | An item is created from those earlier item revision(s) from which it made by merging or editing. |
User-defined relationships can also be defined to identify relationships that are specific to your organization or product.
For two items to be related to each other:
-
The item types must be allowed to be in a valid relationship. This relationship is a parent-child one.
-
The child item must be open and the parent item must be held or open.
At Program Utilities Inc., executable programs, such as their flagship product Process Utility, are usually built from a number of object files, such as Setup, task1, task2, and Finish. The system-defined relationship Made Of is used to relate these types of items.
Request-request relationships
Use request-request relationships to show a dependency or connection between a Dimensions CM request and other Dimensions CM requests.
Dimensions CM Requests can be related to one another by system-defined or user-defined relationships. The system-defined relationships are determined by your process model and cannot be changed.
Note: Non-Dimensions CM requests cannot be related to other requests. For details about configuring and using other request providers, see Configure request providers.
System-defined request-request relationships are:
| Relationship | Description |
|---|---|
| Dependent | A request can be dependent on another request for closure. |
| Information | A request can have an informational relationship to one or more requests. This means that the requests are related for information purposes only. |
User-defined relationships can also be defined to identify relationships that are specific to your organization or product. These relationships are based on the system-defined Dependent or Information types.
For two Dimensions CM requests to be related to each other:
-
The request types must be allowed to be in a valid relationship. This relationship is a parent-child one and must be defined for both Dependent and Information relationship types.
-
For both Dependent and Information types, the child request must be open, and the parent request must be held or open.
-
For the Dependent type, the request types must both have rules enabled or must both have rules disabled. For details, see Use Change Management rules.
-
For the Dependent type, if rules are enabled, the relationship can be established (or dissolved) only if the parent request is in the ANALYSIS or An+Work phase. For details about these phases, see CM rules for request lifecycles.
In-Car Software Inc. has a product set up in Dimensions CM called NAVIGATION. A bug has been found such that the variable direction is sometimes being set to the wrong value. A request is raised for this.
It is found on examination that both the animation and the sound software need to be changed. Two new requests are created for these functional areas, and they are related to the initial request as Dependent.
Item-request relationships
You can relate items and requests in order to track which items need to be changed and to see whether the items have been modified or approved. Items and requests can only be related to one another by system-defined relationships.
Note: Valid relationships are not effective if CM Rules have not been set up for a particular Dimensions CM request type. Therefor any request, whose type rules are disabled, may have any product item revision related to it, provided its item type rules are also disabled.
Item-request relationships are:
| Relationship | Description |
|---|---|
| Affected By | An item (or item revision) can be affected by one or more requests. This means that the item(s) need to be modified to implement the changes required by the request(s). |
| In Response To | An item (or item revision) can be in response to one or more requests. This means that these versions of the items are intended to satisfy the required changes as requested in the request. |
| Information | An item (or item revision) can have an informational relationship to one or more requests. This means that the change is related for information purposes only. |
For a request and item to be related to each other:
-
If CM Rules are switched on, the item and request types must be allowed to be in a valid relationship. This relationship is a parent-child one, with the request type always the parent of the item type.
You can relate any item to any request if CM rules are off.
-
For all relationships types, the item and request must both be open.
-
For the Affected By and In Response To types, the request type and the item type must both have rules enabled or must both have rules disabled. For details, see Use Change Management rules.
-
For the Affected By type, if rules are enabled, then the relationship can only be established (or dissolved) if the Dimensions CM request is in the CREATE, ANALYSIS, or AN+WORK phase.
-
For the In Response To type, if rules are enabled, then the relationship can only be established (or dissolved) if the Dimensions CM request is in the WORK or AN+WORK phase.
In-Car Inc. has decided to change its website to American spelling. Sally was assigned the task of combing through the pages and submitting requests for instances of different spellings. One of the resulting requests is a request to change "catalogue" to "catalog".
The request passed to Jane, the web site manager, who identified the page as Product_List.html. She relates the existing version, revision 3 of this item, to the request as Affected By.
The changes are assigned back to Sally. When she checks out this item to create revision 4 and update the file, the new revision is automatically related to the request as In Response To.
 See also:
See also: