ALM Octane insights
ALM Octane's graphs provide insight cards that help you analyze trends, identify bottlenecks, find correlations, and detect anomalies in your development cycle.
In this topic:
- Insight cards
- Highest cycle times per release insight
- Highest cycle times per release by phase insight
- Highest cycle times insight
- Defects per feature vs. cycle time insight
- Highest resolution times insight
- Resolution time vs. reopen rate
- Automation ROI insights
- Quality risk insights
Insight cards
Insight cards are popup windows associated with Dashboard widgets, that provide insights to help you identify bottlenecks, find correlations, detect anomalies, and better understand what you need to improve in your development cycle. These cards provide you with a summary view in the form of a graph, with a linkable list of the items whose values were included in the graph. Using this information, you can determine where the bottlenecks were in your development cycle and plan how to resolve them.
For example, when working in an Agile environment, it is essential for you to understand the cycle time of your product's features—the time it took R&D to complete a feature. You need to see the time from when features were opened until completion, and where bottlenecks caused a delay in the development process.
It is also important to be able to compare the development cycle time between releases and milestones, to allow you to understand whether you are improving, and if not, then why. It also helps you determine where your bottlenecks occur, and to see the wasted time, helping you understand how to improve your cycle. This information is required in order for you to plan future releases and set release dates. These analytics let you determine the time to market and the effectiveness of your development process. For details about cycle time widgets, see Analyze release progress and quality.
Some of the insight cards reflect the cycle time/resolution time vs. the quality. You can view the trend of speed vs. quality to understand how they correlate with one another. For details about cycle time widgets, see Analyze release progress and quality.
For Return on Investment (ROI) related widgets and insights, see Automation ROI.
You can create multiple widgets to check cycle time and trends for different releases or different feature sizes. For details, see ALM Octane dashboard.
To open an insight card:
-
Add the widget to your dashboard. Widgets with insights contain the Insight icon
 in their description. For details on adding widgets to the dashboard, see Set up the dashboard.
in their description. For details on adding widgets to the dashboard, see Set up the dashboard. - Set the scope for your graph and add it to your Dashboard page. For details, see Configure widget data settings.
- Select the widget. The Insight pane opens. If you close the Insight pane, you can reopen it by clicking the Insight button
 in the top left corner of the graph.
in the top left corner of the graph. -
Drill down by:
- selecting a filter, for example, a release or phase.
- clicking on one of the linked items in the list.
- moving your cursor to the desired part of the graph to view the hover information.
Note: Versions of ALM Octane preceding CP5 (12.55.8) did not collect tracking data. Therefore, if entities were created in earlier versions, their data may not appear in the graphs.
To export your top 100 insights:
- From the Insight pane, click Show more...
- In the toolbar, click the Export to Excel button
 .
.
Highest cycle times per release insight
This insight card opens from the Feature cycle time across releases widget. It shows the top 100 features with the highest cycle time, per release.
To drill down and check the cycle time for a specific release, select a release from the drop down.
To drill down further, click on the feature links to open their details and learn why the cycle time was excessive.

Highest cycle times per release by phase insight
This insight card opens from the Feature cycle time by phase across releases widget.
It shows you a list of the features with the highest cycle time, per release and phase.
To drill down and check the cycle time for a specific phase in a release, select a release and a phase from the drop down.
To drill down further, click on the feature links to open their details and learn why the cycle time was excessive.
Highest cycle times insight
This insight card opens from the Feature cycle time by phase widget.
It shows you a list of the features with the highest cycle time.
To drill down and check the cycle time for a specific phase, select a phase from the drop down.
To drill down further, click on the feature links to open their details and learn why the cycle time was excessive.
Defects per feature vs. cycle time insight
To access this insight card, click the insight button on the Defect Resolution time by phase across releases widget.
In this insight card, you can see a trend of cycle time in comparison with a trend of the quality of the features, which is represented as the average number of defects per feature. Using this comparison/insight you can determine the correlation between speed and quality. For example, If you see an improved cycle time for features, but it also caused a decrease in the quality, you need to further check your processes. You must make sure the decrease in quality is not correlated with the improved features cycle time.
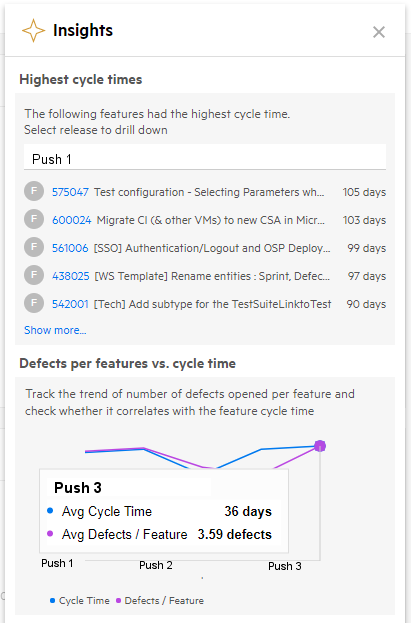
The insight card lists the highest cycle times. To drill down into the results, filter the view to drill down to a specific release and phase. To drill down further, click on their links to open their details and learn why the time was excessive.
To make your insights more relevant, you can create multiple widgets of the same type, filtering each one differently. For example, features with many story points or user stories, will naturally have longer cycle times. In this case, you can create one widget to show only features with 50 or less story points, and another one showing features with 51 or more story points. To do so, open the widget's Scope page and define an additional filter for story points. For details, see Configure widget data settings.
Highest resolution times insight
This insight card opens from the Defect resolution time widgets. It shows you a list of the defects with the highest resolution times.
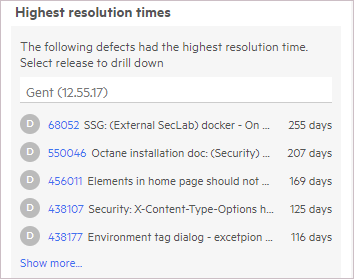
To drill down and check the resolution time for a specific phase, select a release or phase from the drop down.
To drill down further, click on a defect to open its details and learn why the resolution time was excessive.
Resolution time vs. reopen rate
This insight shows the ratio of average defect resolution time across releases vs. the trend of the reopening of defects. The reopen rate refers to defects that were moved from the Fixed to the Opened metaphase or from the Closed to the Opened metaphase.
Tip: You can see the number of reopens by in the Reopens field. If it is not showing, use the Customize fields button  to add it.
to add it.
This trend shown in this insight enables you to check whether the reopen rate correlates with the defect resolution time. For example:
- A reduction in defect resolution may not always be beneficial, if, for example, the quality of the fix is compromised due to a high reopen rate.
- An increase in defect resolution time may not always indicate a problem, if, for example, the reopening ratio has a decreasing trend. This could indicate that more time is being spent on providing higher quality fixes.
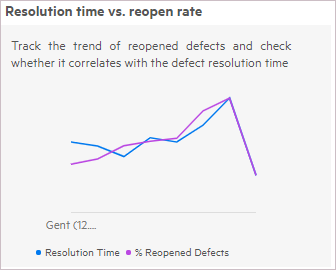
Hover over a point in the graph to see the value at a given point.

Automation ROI insights
To see insights about Automation ROI (Return on Investment), select the Automation ROI widget in the dashboard to display its insights.
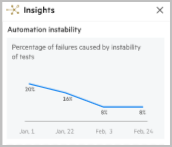
The Automation instability insight provides an indication of whether your automation is stable, and where it can be modified to improve the ROI. If the automation is unstable, it can dramatically lower the automation ROI.
Note: The insight shows the trends of oscillating and unstable tests in the selected pipelines and releases. It is not affected however, by the test automation or application module filters.
This insight describes a trend showing the failures identified as ‘unstable’, as a percentage of all runs in the selected area. The failures are caused by unstable tests. Hover over the graph to see the data for a specific point in time.
For more information about ROI tools, see Automation ROI.
ROI metrics cards
Beneath the Automation instability graph, the Insight pane displays additional informational cards that help let you drill down further into information shown in the graph:
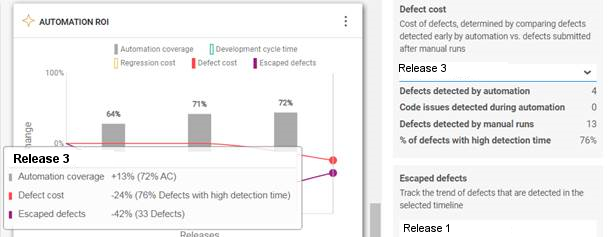
-
Defect cost. The cost of defects, determined by comparing defects detected early by automation vs. defects submitted after manual runs. Defects detected by automation refer to defects reported from automated runs that ran in the selected time frame. Choose a release from the dropdown to show the information relevant to you.
This section shows a summary of:
- Defects detected by automation
- Test failures due to code issues. This value reflects code issues for which defects were not opened. Broken code issues for which defects are not submitted, may significantly affect your cycle time. ALM Octane is able to detect these issues and add them into the calculation of the defect cost. This field requires ALM Octane version 15.1.20 or higher.
- Defects detected by manual runs
- Defects with high detection time. (percentage)

- Development cycle time—Feature CT. The speed of development as determined by feature cycle time. Choose a release or sprint to show the information that interests you.
- Escaped defects. Escaped defects are defects that were not detected by your automation suite nor by your manual testing activities. Investing more in automation aims to decrease defects leaks and improve quality. By investing more in automation you expect to improve the trend and lower the number of escaped defects. This field is only visible when comparing multiple releases—not sprints.
- Regression cost—Manual test executions. The number of manual test executions for the selected application module, release, or sprint. Choose a release or sprint from the dropdown to show the information that interests you.
Quality risk insights
Within the Quality module, we use the Risk page to locate areas where functionality is not sufficiently tested. For details, see Quality risk analytics.
 See also:
See also: