Rule examples
Examples of creating rules are listed below.
Count the number of times defects are re-opened
For the purpose of improving quality processes, you can track the number of times defects are re-opened after being set to Fixed.
- In the Defect entity, create a Reopen Counter field of the Integer field type. For details, see Fields.
- Create a new rule for the Defect entity.
-
On the Action tab, select the following values.
Setting Value Action Set field value Timing When saving an entity
Field Reopen Counter Increment value by 1 -
On the Condition tab, define the following conditions, combined by AND.
Field Operator Value Phase Current = Opened Phase Original ≠ New
Set the Epic level field
The Epic level field determines whether an epic is automatically synchronized with the Strategy module, or whether the epic exists in the Agile module only. For details, see Epics.
You can set the Epic level field automatically based on the epic type, either business or architecture. For example, if the epic type is architecture, you may want to keep the epic local to the Agile module.
For this, define the business rule as follows:
-
Action:
Field Value Action Set field value Timing When creating an entity Field to set Epic level Change > Set value Local
-
Condition: Epic type ≠ Business
When the business rule is turned on, the level of a new epic is automatically set to Local if the epic type is not business.
Record the Last Modifier of a manual test
It can be useful to know who made the last change to a manual test. You can create a rule to record this information in a user-defined field. The field is populated when specified changes are made to the manual test.
- In the Manual Test entity, create a Last Modifier field of the User field type. For details, see Fields.
- Create a new rule for the Manual Test entity.
-
On the Action tab, select the following values.
Setting Value Action Set field value Timing When changing a value
Note: Select the fields for which a change to their values records a change to the Last Modifier field.
Field to set Last Modifier Set value [Current User]
Use different lookup lists
Create a rule that uses a different lookup list for a feature's Customer, depending on the feature's release.
For example, if a feature is scheduled for release 5.1, the available Customer values are the customers signed up for a Beta program, instead of the standard list of customers.
-
Prerequisite: Create a list of customers named Beta_customers.
-
Define a business rule for the Feature entity as follows:
-
Condition: Release = 5.1.
-
Action: Modify lookup list for the field Customer. Select Beta_customers in the List field.
-
Set a subset of a lookup list
Depending on the current team, certain item origins for defects are not available. For example, if a certain team only works with OpenText Application Quality Management and OpenText Core Software Delivery Platform, the item origin for that team's defects cannot be Service Anywhere or Jira. You can create a rule that makes only a sub-list of the current lookup list available, based on the team.
-
Condition: The Team field is a specific value.
-
Action: Select the Item Origin values that are relevant to that team.
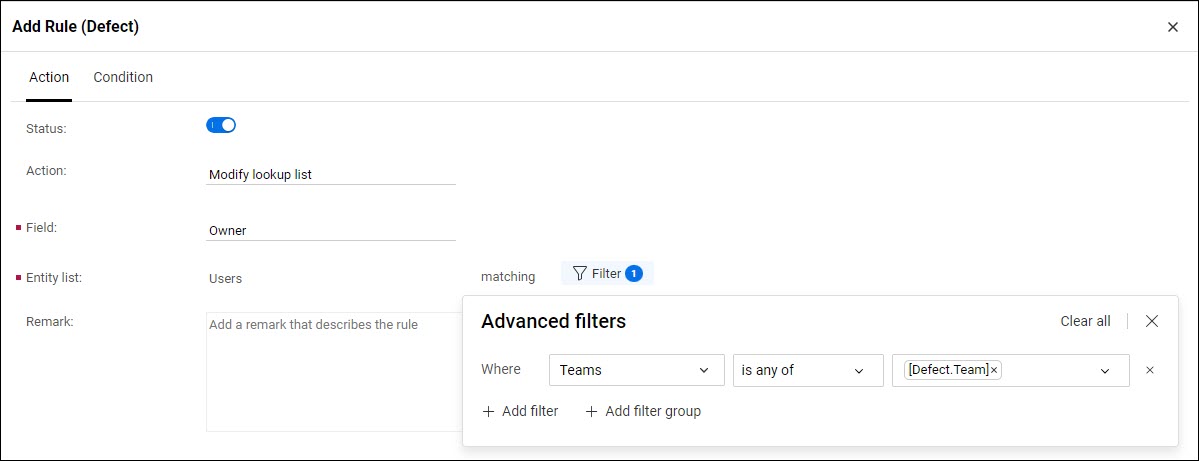
Modify available values for a reference field
You can modify the available values for a reference field, such as Release or Team, to include only the items that match a filter you define. You can also filter the available values for the reference field of an item, based on the attributes of the item.
For details on reference fields, see Reference fields.
For details on setting up the filter, see Advanced filters.
Example 1:
If a feature's Product field is set to Product A, you can filter the available values for the feature's Team field to include only teams assigned to Product A.
For example, if a feature's Product field is set to Product A, you can filter the available values for the feature's Team field to include only teams assigned to Product A.
Define a business rule for the Feature entity as follows:
-
Condition: Product = Product A
-
Action: Modify lookup list of the Team field to include only teams where Product includes Product A.
Example 2:
If you set up a business rule for the Issue entity, you can filter the available values for the Owner field based on the value of the Issue's Team field ([Issue.Team]). This means that the Owner field offers only users from the Team assigned to the issue.
Make fields required
Make the testing tool type required to prevent empty values for automated tests.
-
Condition: Testing tool type is empty.
-
Action: The Testing tool type field is required.
Set default field values (Set Field Value)
To make sure each manual test is assigned to an application module, set the Application modules field value to a default application module for all empty statuses.
-
Condition: If the Edit mode for the test is New, it means the test was just created
-
Action: Set the Application modules field to General.
Set a value when a related item changes (Set Field Value)
Automatically set a user story to Done when all its child tasks are done (DoD).
-
Condition: The number of child tasks with the phase New or In Progress is zero. Use the following values to formulate this condition:
Field Value Operand Child task count Operator {filter = Phase: ( New, In Progress ) } Equals 0 -
Action: Set the Phase field for the user story to Done.
Consider the following:
-
The transition from current phase to Done is possible based on the workflow. For example, if the phase of a user story is New, it cannot be promoted to Done.
-
The Set Field Value rule does not validate to make sure required fields have values. For example, if Severity is a required field when promoting to Done, the promotion rule still updates the phase to Done even if Severity is blank.
-
The rule overrides manual changes. When you define this rule, there are no exceptions. You cannot, for example, manually modify user story's phase if all its related tasks are done. The next time the rule runs, the phase is reset to Done.
-
When the rule runs, its actions are performed by an internal system user.
Copy values from fields for related items (Set Field Value)
You can create a business rule action to automatically populate system and user-defined fields, based on the fields for related items. For example, fields for backlog items can be automatically populated based on the corresponding fields for their parent feature.
Note: You can copy field values from related items that are single and multi-value reference fields.
When copying from multiple related items, consider the following.
| Use case | Details |
|---|---|
| Copying from a multi-value cross field to a multi-value field |
The target field is populated with source field values from all the related items. For example, copy tags to a defect from its related requirements. When the rule is triggered, the defect's Tags field is the collection of tags defined for all the related requirements. |
| Copying from a single-value cross field to a single-value field |
The business rule is triggered only if the source field has the same value in all the related items. For example, you need the defect's Owner field to be auto populated with the Author value of related application modules. In this case, the rule is triggered only if all the application modules, defined for this defect, have the same author. |
Create a rule action
Define the rule action as follows.
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| Action | Set field value. |
| Timing |
Select any suitable timing option. |
| Field to set | Select the field whose value you want to populate automatically. |
| Change > Copy value from field |
Select a related item's cross field whose value should be copied to the Field to change. Note: The Select field dialog box includes the following fields:
If necessary, you can create compatible user-defined fields. For details, see Fields. |
When the business rule is turned on, the source field value is copied to the target field of a related item. If the target field is already populated, a new value replaces the original value.
Show or hide specific fields in entity forms
You can create a business rule action to show or hide specific entity fields based on workspace-specific needs. This addresses the challenge of managing shared forms across workspaces, where different teams require unique fields.
The following table provides some use cases.
| Admin type | Use case |
|---|---|
| Workspace admin |
Needs to create various different forms for each entity type, where the main fields and sections are common to all forms, but some specific fields differ. For example, the workspace admin might need one form for security defects which displays the security libraries field, and another for regression defects which displays the regression from version field. A workspace admin can create each form from the shared defect form, and then show or hide specific fields according to the defect type. |
| Space admin |
Needs to enforce the display of specific fields in the workspace entity forms. For example, the space admin might need to enforce the display of specific fields on workspace forms, ensuring compliance with global standards and reporting requirements. A space admin can define forms and business rules with mandatory fields. Workspace admins can then force specific fields to appear on the workspace form and certain business rules to apply and take precedence. |
Trigger webhooks (call a URL)
For webhook integration with another application when an entity is created, deleted or updated, you can use a Trigger Webhook rule to POST a request to an endpoint URL. The service at the URL receives the call and processes the request.
Condition: <None>
Actionable upon: New, Update, Delete
Action: POST entity information to the endpoint URL: http://myServer:8081/myAPI.
For details on setting up Trigger Webhook rules to POST information to endpoint URLs as a result of an event, see Trigger webhooks for other applications.
Switch forms
When a tester creates a defect to report a bug, organizational policy dictates that the tester should be able to view and edit the following fields: Description and Severity.
Similarly, when a developer starts fixing a defect, the developer must be able to view and edit the following fields: Fixed on, Fixed in Build, and Owner.
Define two rules:
-
Rule 1: Sets a form for developers.
Condition: If the team is the Developer team...
Action: The form for developers is used.
-
Rule 2: Sets a form for testers.
Condition: If the team is the Tester team...
Action: The form for testers is used.
Send an email when an item is updated
When a user story, defect, or other item changes its status, you may want to be notified that such an item has been updated.
To do this, define a business rule in one of the following ways:
-
If you want to be notified of any change in a specific field, such as the phase of an item, select the field and set Is Modified as the operator for the field.
-
If you want to be notified of a change in a specified field to a specific value, such as a defect moving from Opened to Fixed, select the field and set the operator Original = for the previous value. Then, add another line using AND, select the same field, and set the operator to = for the new value.
Prevent developers from closing a defect
You may want to prevent developers from closing defects, to ensure that the defect solution is reviewed by other stakeholders before the defect is closed. You can create a workflow rule that blocks this transition.
Create the rule from the Workflow tab for the entity. This way, the From and To phases for the transition are already entered for you. Select the transition between Proposed Closed and Closed, and add a rule using the Rules pane.
Condition: If the Current User Role includes Team Member...
Action: Block transition from Proposed Closed to Closed.
Prevent testers from creating defects on old releases
Testers work on different releases.
First, ask your space admin to make sure that the tester has create/edit permissions for defects. For details, see Roles and permissions.
Then, add an Alert User rule with a condition that lists the releases for which the tester cannot update defects.
If the condition in the rule evaluates to true, the rule alerts the user that the updates violate the specified condition and prevents all updates to the defect.
Action: Alert the user when creating, modifying or deleting a defect if the condition indicates a problem (meaning, the condition evaluates to true).
Condition: If the Current User Role includes Tester, and Release equals a forbidden release, the condition evaluates to true. The user is alerted and updates are prevented.
Notify the assigned tester when a test is ready to run
When the run order of manual tests in a test suite is enforced, a test in the suite cannot be run until all preceding test runs have been completed. For details, see Enforce manual test run order.
You can create a rule to automatically notify the assigned tester when a test in the suite is ready to run. Add a rule for the Manual Run entity and set the fields as follows:
Action tab
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| Action | Send email |
| Submission mode | Update |
| Send to | Run by |
| Email subject |
Test run is ready for execution. Note: Modify this text as needed. |
Condition tab
| Field | Operator+Value |
|---|---|
| Blocked by previous run | is modified |
| Blocked by previous run | Current = No |
Lock completed manual test runs
Preventing changes to test evidence is critical from an auditing perspective. Using a business rule, you can lock test runs and run steps when the run or suite run is marked as finalized.
The sequence is described in the following table.
| Step | Description | Details |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | After a suite run or test run has been fully executed, the tester flags the item as "finalized". |
Prerequisite: Create a boolean or single-selection custom field as a "finalized" flag on the Suite Run or Manual Run entity. For details, see Fields. The business rule example below refers to a custom field called Is Finalized. |
| 2 | Following step 1, a business rule sets the test runs' Native status to read-only. |
See the business rule details below. Note: Step 3 works on the basis of the Native status field becoming read-only. Therefore, the business rule should be defined on that field alone. |
| 3 | Following step 2, the run steps are automatically set as read-only. |
Finalized run steps cannot be edited. You can still report defects and add attachments to locked steps. Note: The locking behavior depends on the space parameter DISABLE_RUN_STEPS_EDIT_WHEN_RUN_STATUS_READONLY. For details, see Configuration parameters. |
Create a rule for the Manual Run entity as follows:
Action tab
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| Action | Make read-only |
| Field | Native status |
Condition tab
| Field | Operator+Value |
|---|---|
|
Is Finalized or Suite run.Is Finalized Note: "Is Finalized" is an example of a custom boolean or single-selection field created in the Suite Run or Manual Run entity. |
Current = Yes |
Assign data access categories
You can set up data access control in your shared space to allow users to access only the data that they are entitled to see. For details, see Data access control.
You can create business rules that assign data access categories to items when they're created or changed. This business rule is supported for requirements, defects, and manual tests.
Action tab
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| Action | Set field value |
| Timing |
When creating an entity or When changing a value. To update an item both upon creation and during editing, create two separate rules. |
| Field to set | Data access categories |
| Change |
Set value. From the list, select the data access categories that you want to include in the rule. |
Condition tab
| Row | Field | Operator | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| #1 | Current User Role | include | [Select the relevant roles] |
Tip: To avoid situations where items are without a data access category, define a default category and assign it using a dedicated rule. Run the default rule first, so that it does not override specific item categories. For details, see Data access control.
 See also:
See also: