WPF/Silverlight Custom Support Setup Dialog Box (Version 2021 R1 or earlier)
Relevant for version 2021 R1 or earlier
This topic describes WPF/Silverlight Custom Support Dialog Box for the version 2021 R1 or earlier. For version 2022 or later, see WPF Custom Support Setup Dialog Box (Version 2022 or later).
This dialog box opens when you select the OpenText Functional Testing WPF Custom Support template to create an OpenText Functional Testing Extensibility project in Microsoft Visual Studio.
The Custom Server Setup dialog box enables you to provide specifications that describe the support that you want to create. When the extensibility project is created in Visual Studio, its files are created with the basic content, infrastructure, and references required to create the support you described.
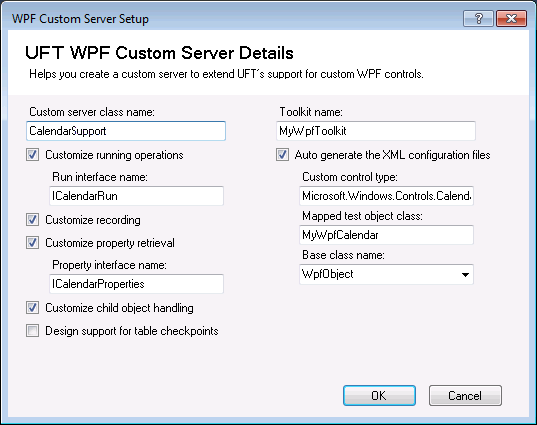
This image displays a WPF Custom Server Setup dialog box. The options on a Silverlight Custom Server Setup dialog box are identical to the ones shown below. Only the dialog box titles and the list of available base classes are different for Silverlight.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| To access |
|
| Important information | To successfully create a project using the UFT Silverlight CustomServer template, you must have the Microsoft Silverlight Tools for Visual Studio installed. |
| Relevant tasks | How to create support for a Custom Toolkit (Version 2021 R1 or earlier) |
| See also |
User interface elements are described below:
UI Elements | Description |
|---|---|
| Custom server class name | The name of the custom server class to create in the new project. Note: By default, this name is used to create the default values for Run interface name, Property interface name, and Mapped test object class. If you have not changed these values, modifying the Custom server class name modifies them as well. |
| Customize running operations | Indicates that you want to design or override implementation for running test object operations on the control. If you select this option, the Run interface that you specify is defined and tagged with the RunInterfaceAttribute. In the custom server class, the interface is implemented with a method stub for an example test object operation. The example test object operation is also added to the project's test object configuration file. |
| Run interface name | The name of the interface in which you want to implement support for the test object operations. Available only when Customize running operations is selected. |
| Customize recording | Indicates that you want to design support for recording test object operations on the control. If you select this option, the custom server class is defined to implement the IRecord interface and includes method stubs for the interface's methods. Note: The links in this section link to the Mercury.QTP.WPF.CustomServer namespace section in the Custom Support API Reference. For the most part, the information there is relevant for Silverlight as well, and is identical to the information provided in the Mercury.QTP.Slv.CustomServer namespace section. The IRecord interface is different in the two namespaces. See this link for information on the IRecord interface in the Mercury.QTP.Slv.CustomServer namespace. |
| Customize property retrieval | Indicates that you want to design or override implementation for retrieving identification property values from the control. If you select this option, the Property interface that you specify is defined and tagged with the CustomPropInterfaceAttribute. In the custom server class, the interface is implemented with a method stub for an example identification property. The example identification property is also added to the project's test object configuration file. |
| Property interface name | The name of the interface in which you want to implement support for property value retrieval. Available only when Customize property retrieval is selected. |
| Customize child object handling | Indicates that you want OpenText Functional Testing to treat some of the custom control's child objects as an integral part of the control and not as independent objects. If you select this option, a preliminary implementation of the IsKnownPartOf method in the IComponentDetector interface is created in the custom server class. Implement the method to return true for the relevant child objects. |
| Design support for table checkpoints | Indicates that you want the standard checkpoints and output values that OpenText Functional Testing creates on your test object to be table checkpoints and output values. If you select this option, a preliminary implementation of the ItableVerify interface is created in the custom server class. Implement this interface according to your needs. |
| Toolkit name | A name for the environment, or set of controls, that you want to support with this toolkit support set. You may want the name to indicate whether this is a WPF or Silverlight toolkit. After you deploy your support, OpenText Functional Testing displays this name in the Add-in Manager as a child node under the WPF add-in node, enabling the user to specify whether to load support for this environment. In the new project created, the toolkit name is used to create the configuration file names, and entered in the PackageName attribute of the TypeInformation element in the test object configuration file (if you select Auto generate the XML configuration files). It is also used for the root namespace of the project. |
| Auto generate the XML configuration files | Indicates that in the new project created, a toolkit configuration file and test object configuration file should also be created. The files are created with basic definitions, according to the details you specify in this dialog box. In a toolkit support set, the definitions for all of the controls that you want to support are included in one toolkit configuration file, and one test object configuration file. On the other hand, you design a separate custom server for each control you support. Therefore, if you use the template to create additional custom servers, you might not want to generate additional XML files. Alternatively, you can decide to generate the XML configuration files as well, and then copy the information from these new files to your main configuration files. |
| Custom control type | The name of the custom control type for which you want to develop support. For Silverlight: A full type name, including namespaces. For WPF: This can be one of the following:
Note: In most cases, the full type name is sufficient. You can use the more complex name when the same control is included in more than one assembly, for example, when your application includes different versions of the same control. |
| Mapped test object class | The test object class that you want OpenText Functional Testing to use to represent the custom control. In the new project created, a basic definition for this new test object class is created in the test object configuration file (if you select Auto generate the XML configuration files). |
| Base class name | The test object class that your new test object class extends. Select from the list of built in OpenText Functional Testing test object classes, or enter a name of a test object class that you defined in a WPF or Silverlight Add-in Extensibility test object configuration file. (WPF test object classes need to extend other WPF test object classes, and Silverlight test object classes need to extend other Silverlight test object classes.) Default: WpfObject or SlvObject |