RabbitMQ Connector Configuration
The RabbitMQ connector connects to a RabbitMQ broker using the AMQP-0-9-1 protocol.
Example of connector configuration in sv-lab.json:
"connector": [
{
"id": "connector",
"connectorType": "rabbitMq",
"properties": {
"brokerUri": "amqp://localhost:5672/",
"username": "guest",
"password": "guest"
}
}
],Endpoint configuration
The client and service can communicate through a RabbitMQ exchange:

In a simpler setup, they can use only a queue without exchange:

The communication can be one-way or the request-response message exchange pattern can be in place:
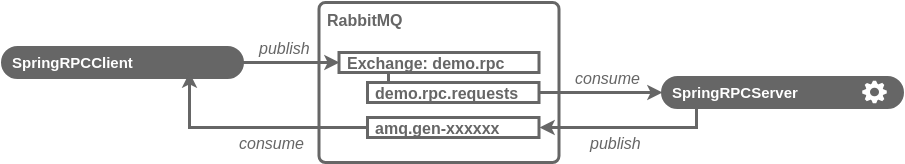
Depending on intended modes of virtual service and message exchange pattern used the RabbitMQ endpoint is configured with up to 4 destinations:
| Destination | Used by virtual service for | Direction | Service modes |
|---|---|---|---|
| virtual request | receiving requests from clients | INPUT | FORWARD, SIMULATE |
| virtual response | sending responses to clients | OUTPUT | FORWARD, SIMULATE |
| real request | sending requests to real service | OUTPUT | FORWARD, INVOKE |
| real response | receiving responses from real service | INPUT | FORWARD, INVOKE |
Each of the endpoint destinations can be configured to use either an exchange or a static or dynamic queue. It is possible to combine exchanges with queues in one endpoint.
- Exchange
- The virtual service receives messages from the
virtualRequestQueueand/or therealResponseQueue. ThevirtualRequestExchangeand/orrealResponseExchangecan be optionally provided so that SV will declare the exchange for client and/or the real service. - The virtual service sends messages to the
virtualResponseQueueand/orrealRequestQueuewith routing key specified in theamqp:routing-keymessage header or the correspondingvirtualResponseDefaultRoutingKeyorrealRequestDefaultRoutingKey. - When the provided exchange and/or queue does not exist, SV will declare it and bind the provided static queue to the exchange with one or more binding keys provided as a comma separated list of keys.
- The binding keys can use simple
*and multiple#wildcards.
- The virtual service receives messages from the
- Static queue
- The
virtualRequestQueueandrealResponseQueueis used to receive input messages. - The
virtualResponseQueueandrealRequestQueueis used to send output messages. The static destination can be overriden by theamqp:reply-toheader of corresponding request message. - When the queue does not exist, SV will declare it.
- The
- Dynamic queue
- Used in request-response message exchange pattern when the queue for
response is provided with each request using
amqp:reply-toheader. - The corresponding
virtualResponseQueueorrealRequestQueuedestination of endpoint is omitted when using dynamic queue or it can contain a default, fallback destination to target the message in case theamqp:reply-toheader is missing.
- Used in request-response message exchange pattern when the queue for
response is provided with each request using
Note
Some optional destination properties are not used for message routing but for SV Lab to declare queues and or exchanges and to bind queues to exchanges when the client and/or real service expects that the destinations exist.
Note
The queues and exchanges declared by SV Lab are deleted when the virtual lab is undeployed.
RabbitMQ connector configuration properties
Mandatory properties are bold. Other properties are optional.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| brokerUri | (string) The broker URI, i.e. amqp://localhost:5672/myVirtualHost or amqps://localhost:5671/ |
| username | (string) Username for authentication with broker. |
| password | (string) Password for authentication with broker. |
RabbitMQ endpoint configuration properties
Mandatory properties are bold. Other properties are optional.
| Property | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| virtualRequestQueue | (string) The queue for receiving requests from clients. (1) | |
| virtualRequestQueueDurable | false | (boolean) Whether the queue should be declared as durable. (3) |
| virtualRequestQueueExclusive | false | (boolean) Whether the queue should be declared as exclusive. (3) |
| virtualRequestQueueAutodelete | false | (boolean) Whether the queue should be declared with autodelete flag. (3)(6) |
| virtualRequestExchange | (string) The exchange to declare for receiving requests from clients. Plain virtualRequestQueue can be used without exchange. (2) |
|
| virtualRequestExchangeType | (string) Exchange type used when the exchange is being declared. (3)(4) | |
| virtualRequestExchangeDurable | false | (boolean) Whether the exchange should be declared as durable. (3) |
| virtualRequestExchangeAutodelete | false | (boolean) Whether the exchange should be declared with autodelete flag. (3)(6) |
| virtualRequestBindingKeys | (string) Comma-separated list of keys to bind receiving queue to exchange. (3) | |
| virtualResponseQueue | (string) The queue where clients receive responses. Optional, the client can provide response queue with replyTo header. (1) |
|
| virtualResponseQueueDurable | false | (boolean) Whether the queue should be declared as durable. (3) |
| virtualResponseQueueExclusive | false | (boolean) Whether the queue should be declared as exclusive. (3) |
| virtualResponseQueueAutodelete | false | (boolean) Whether the queue should be declared with autodelete flag. (3)(6) |
| virtualResponseExchange | (string) The exchange for sending responses to clients. Plain virtualResponseQueue can be used without exchange. (2) |
|
| virtualResponseExchangeType | (string) Exchange type used when the exchange is being declared. (3)(4) | |
| virtualResponseExchangeDurable | false | (boolean) Whether the exchange should be declared as durable. (3) |
| virtualResponseExchangeAutodelete | false | (boolean) Whether the exchange should be declared with autodelete flag. (3)(6) |
| virtualResponseBindingKeys | (string) Comma-separated list of keys to bind receiving queue to exchange. (3) | |
| virtualResponseDefaultRoutingKey | (string) Default routing key for sending simulated responses to clients through exchange. (5) | |
| realRequestQueue | (string) The queue where service receives requests. Optional, the client can provide a queue with replyTo header for solicit response in invocation mode. (1) |
|
| realRequestQueueDurable | false | (boolean) Whether the queue should be declared as durable. (3) |
| realRequestQueueExclusive | false | (boolean) Whether the queue should be declared as exclusive. (3) |
| realRequestQueueAutodelete | false | (boolean) Whether the queue should be declared with autodelete flag. (3)(6) |
| realRequestExchange | (string) The exchange for sending requests to service. Plain realRequestQueue can be used without exchange. (2) |
|
| realRequestExchangeType | (string) Exchange type used when the exchange is being declared. (3)(4) | |
| realRequestExchangeDurable | false | (boolean) Whether the exchange should be declared as durable. (3) |
| realRequestExchangeAutodelete | false | (boolean) Whether the exchange should be declared with autodelete flag. (3)(6) |
| realRequestBindingKeys | (string) Comma-separated list of keys to bind the queue to exchange. (3) | |
| realRequestDefaultRoutingKey | (string) Default routing key for sending simulated responses to clients through exchange. (5) | |
| realResponseQueue | (string) The queue to receive responses from service. | |
| realResponseQueueDurable | false | (boolean) Whether the queue should be declared as durable. (3) |
| realResponseQueueExclusive | false | (boolean) Whether the queue should be declared as exclusive. (3) |
| realResponseQueueAutodelete | false | (boolean) Whether the queue should be declared with autodelete flag. (3)(6) |
| realResponseExchange | (string) The exchange to declare for receiving responses from service. Plain realResponseQueue can be used without exchange. (2) |
|
| realResponseExchangeType | (string) Exchange type used when the exchange is being declared. (3)(4) | |
| realResponseExchangeDurable | false | (boolean) Whether the exchange should be declared as durable. (3) |
| realResponseExchangeAutodelete | false | (boolean) Whether the exchange should be declared with autodelete flag. (3)(6) |
| realResponseBindingKeys | (string) Comma-separated list of keys to bind the queue to exchange. (3) |
Notes:
- [1] When specified and the queue does not exist, the queue is declared by SV.
- [2] When specified and the exchange does not exist, the exchange is declared and the queue bound to it with provided binding keys.
- [3] Used only when the corresponding queue or exchange does not exist and it is being declared.
- [4] One of
direct,fanout,topicorheaders. Exchange types are explained in RabbitMQ documentation. - [5] Used when sending simulated message through exchange (response in
simulation, request in invocation mode) and the model message does not
specify routing key via the
amqp:routing-keyproperty. - [6] The exchanges and queues declared by SV Lab get deleted when the virtual gets undeployed regardless of the autodelete attribute. Setting the autodelete attribute to true may cause unintended behavior when client disconnects and reconnects to RabbitMQ broker while virtual lab is deployed and the exchange and queue used by client get deleted by broker.